Two Moons Of Uranus: Titania And Oberon. Both Moons Were Discovered By William Herschel In 1787.
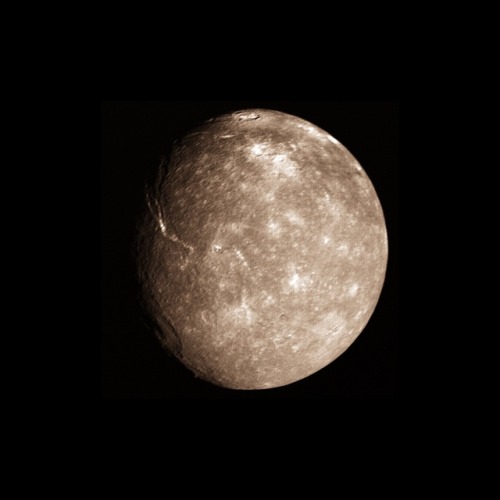

Two moons of Uranus: Titania and Oberon. Both moons were discovered by William Herschel in 1787.
Credit: NASA/JPL
More Posts from Xnzda and Others

“For small creatures such as we the vastness is bearable only through love.” – Carl Sagan
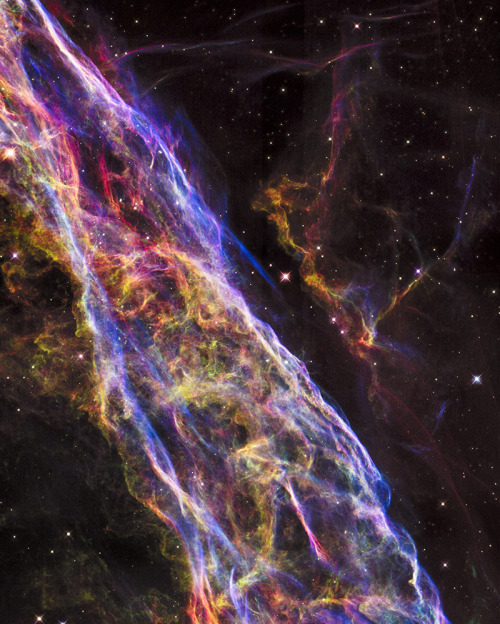

Veil Nebula Supernova Remnant
via NASA Hubble Space Telescope has unveiled in stunning detail a small section of the expanding remains of a massive star that exploded about 8,000 years ago.
Called the Veil Nebula, the debris is one of the best-known supernova remnants, deriving its name from its delicate, draped filamentary structures. The entire nebula is 110 light-years across, covering six full moons on the sky as seen from Earth, and resides about 2,100 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus, the Swan.
This view is a mosaic of six Hubble pictures of a small area roughly two light-years across, covering only a tiny fraction of the nebula’s vast structure.
This close-up look unveils wisps of gas, which are all that remain of what was once a star 20 times more massive than our sun. The fast-moving blast wave from the ancient explosion is plowing into a wall of cool, denser interstellar gas, emitting light. The nebula lies along the edge of a large bubble of low-density gas that was blown into space by the dying star prior to its self-detonation.
Image Credit: NASA/ESA/Hubble Heritage Team
on the first day of class my astronomy professor asked us why the night sky was dark. if our universe is infinite, how can there be spaces between the stars? he didn’t answer the question until the last day– because our universe is relatively young, and is still growing. it is finite. not enough stars or galaxies have been formed to fill up the entire night sky.
but what that means to me is that somewhere, in an older universe, the night sky looks like a tapestry of diamonds. somewhere darkness is pale white and glittering. imagine being so surrounded. i haven’t gotten that image out of my head ever since– you could never navigate under such a sky but god it sounds lovely









The best photographs that the Hubble space telescope has ever taken.
1. Sombrero galaxy
2. V838 Monocerotis
3. Jupiter’s great red spot
4. Carina nebula
5. Interacting galaxies
6. Pillars of creation
7. Cat’s eye nebula
8. Planetary Nebula NGC 5189
9. Abell 2744 Frontier Field
(Source)

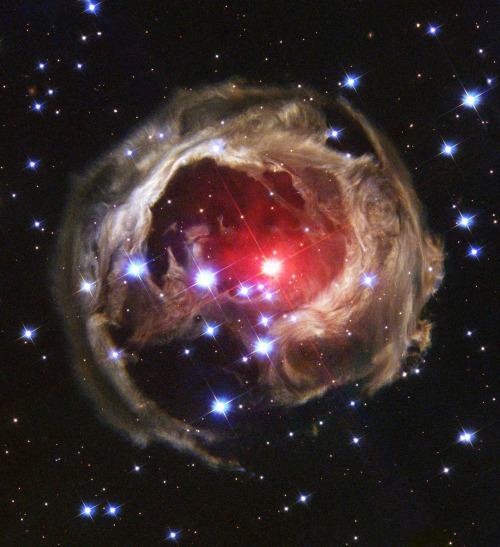
Pew! Pew! Pew!
Imagine slow-motion fireworks that started exploding 170 years ago and are still continuing. This type of firework is not launched into Earth’s atmosphere, but rather into space by a doomed super-massive star, called Eta Carinae.
Enjoy the the latest view from our Hubble Space Telescope.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
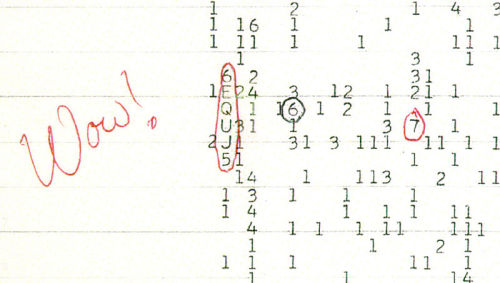
The Wow! signal.
A signal sequence that lasted for 72 seconds in 1977 but has never been seen again. The signal appeared to come from a globular cluster in the Sagittarius constellation, but to this day no definite answer for where the signal originated can be given.
-
 ooooxsblog liked this · 3 weeks ago
ooooxsblog liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 soniciselectricc liked this · 2 months ago
soniciselectricc liked this · 2 months ago -
 legendarykidherringsludge liked this · 2 months ago
legendarykidherringsludge liked this · 2 months ago -
 amandajasmine reblogged this · 3 months ago
amandajasmine reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 blackcatcore reblogged this · 3 months ago
blackcatcore reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 vvitcherys reblogged this · 3 months ago
vvitcherys reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 unregistered-hypercam002 liked this · 3 months ago
unregistered-hypercam002 liked this · 3 months ago -
 luvbites liked this · 3 months ago
luvbites liked this · 3 months ago -
 fullheartss liked this · 3 months ago
fullheartss liked this · 3 months ago -
 subtotem reblogged this · 3 months ago
subtotem reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 prince-of-lesbos liked this · 3 months ago
prince-of-lesbos liked this · 3 months ago -
 oflline reblogged this · 3 months ago
oflline reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 oflline liked this · 3 months ago
oflline liked this · 3 months ago -
 highonlife22 reblogged this · 3 months ago
highonlife22 reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 ohfallingstar reblogged this · 3 months ago
ohfallingstar reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 finnstansonly reblogged this · 5 months ago
finnstansonly reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 digitaloves reblogged this · 5 months ago
digitaloves reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 shyspice liked this · 9 months ago
shyspice liked this · 9 months ago -
 kawaiidesu reblogged this · 1 year ago
kawaiidesu reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 kawaiidesu liked this · 1 year ago
kawaiidesu liked this · 1 year ago -
 craftyrebelwitch liked this · 1 year ago
craftyrebelwitch liked this · 1 year ago -
 scorpiosource-moved reblogged this · 1 year ago
scorpiosource-moved reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 hxvnted-rxse reblogged this · 1 year ago
hxvnted-rxse reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 nessieac liked this · 1 year ago
nessieac liked this · 1 year ago -
 iwillruletheuniverse reblogged this · 1 year ago
iwillruletheuniverse reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 ohfallingstar reblogged this · 1 year ago
ohfallingstar reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 catastrophic-kiss reblogged this · 1 year ago
catastrophic-kiss reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 kostassus liked this · 1 year ago
kostassus liked this · 1 year ago -
 lostenvelope reblogged this · 1 year ago
lostenvelope reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 dollhandinfection reblogged this · 1 year ago
dollhandinfection reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 rocksopera reblogged this · 1 year ago
rocksopera reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 zombiequeer liked this · 1 year ago
zombiequeer liked this · 1 year ago -
 westernstarofthenorth reblogged this · 1 year ago
westernstarofthenorth reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 westernstarofthenorth liked this · 1 year ago
westernstarofthenorth liked this · 1 year ago -
 squirrel666 reblogged this · 1 year ago
squirrel666 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 screamingwombatgirl reblogged this · 1 year ago
screamingwombatgirl reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 screamingwombatgirl liked this · 1 year ago
screamingwombatgirl liked this · 1 year ago -
 no-th0ts-just-vibes reblogged this · 1 year ago
no-th0ts-just-vibes reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 no-th0ts-just-vibes liked this · 1 year ago
no-th0ts-just-vibes liked this · 1 year ago -
 anynameisbetterthanmyfirstone liked this · 1 year ago
anynameisbetterthanmyfirstone liked this · 1 year ago -
 just-a-pointless-being reblogged this · 1 year ago
just-a-pointless-being reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 livmanchuk reblogged this · 1 year ago
livmanchuk reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 blueeunderthesamesky reblogged this · 1 year ago
blueeunderthesamesky reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 sticktoyourcatss reblogged this · 1 year ago
sticktoyourcatss reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 godmirror reblogged this · 1 year ago
godmirror reblogged this · 1 year ago



![Swirls And Colors On Jupiter From Juno [3709x2772]](https://64.media.tumblr.com/a02cf38823ae6cfdd3b32a401035a7a3/tumblr_pij9hl3nnd1rcl722o1_500.jpg)
