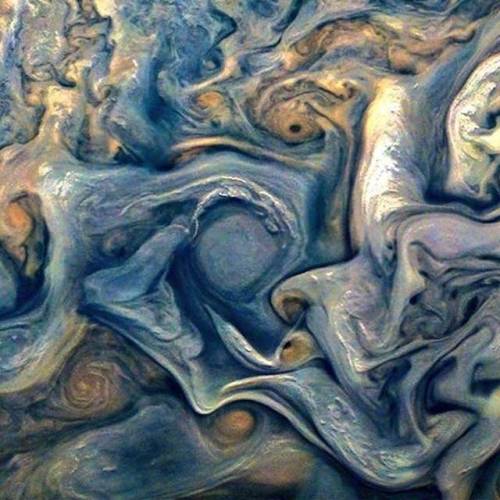
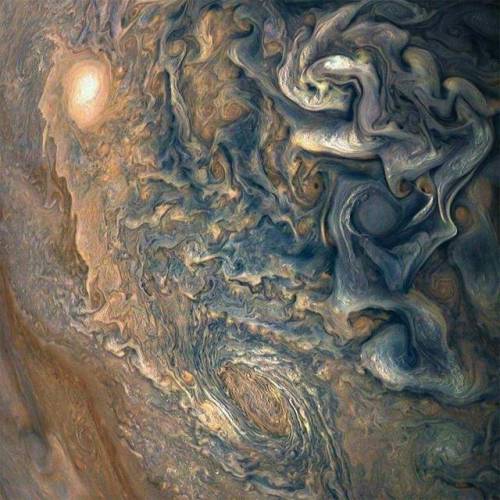
Pew! Pew! Pew!

Pew! Pew! Pew!
Imagine slow-motion fireworks that started exploding 170 years ago and are still continuing. This type of firework is not launched into Earth’s atmosphere, but rather into space by a doomed super-massive star, called Eta Carinae.
Enjoy the the latest view from our Hubble Space Telescope.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Xnzda and Others

M94: Bursting With Stars
Located about 16 million light-years away, this new Hubble image shows the sparkling galaxy Messier 94. You’ll notice the bright ring (or starburst ring) around Messier 94 where new stars are forming at a high rate. The cause of this star-forming region is thought to be a pressure wave going outwards from the galactic center, compressing the gas and dust in the outer region. The compression of material means the gas starts to collapse into denser clouds. Inside these dense clouds, gravity pulls the gas and dust together until temperature and pressure are high enough for stars to be born. (Image credit: NASA / ESA / Hubble)

Remains of supernova explosion Cassiopeia A most recent supernova in Milky Way








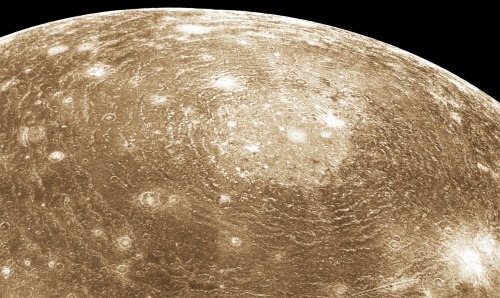
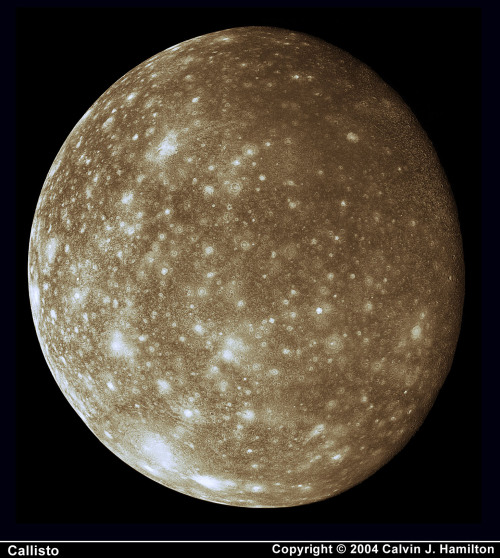
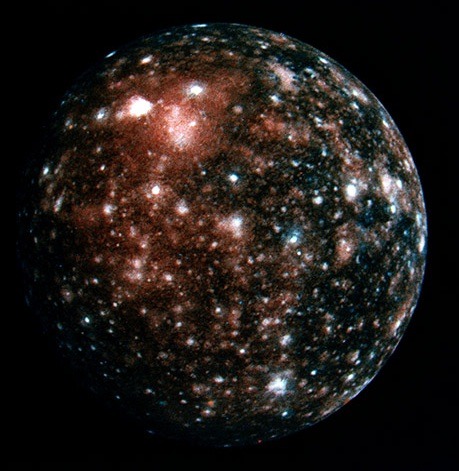
All here… Sorry, Pluto, you don’t belong here
PS: I do follow back

Looking like an elegant abstract art piece painted by talented hands, this picture is actually a NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image of a small section of the Carina Nebula.
Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA

In this amazing Hubble Space Telescope image, a blue bubble-like nebula surrounds a Wolf–Rayet star WR 31a, located about 30,000 light-years away in the constellation of Carina (The Keel). Wolf–Rayet stars are the most massive and brightest stars known, and their lifecycle is only a few hundred thousand years — a blink of an eye in cosmic terms.
Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt
-
 hopefuldreamers-world reblogged this · 1 year ago
hopefuldreamers-world reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 hopefuldreamers-world liked this · 1 year ago
hopefuldreamers-world liked this · 1 year ago -
 shibushiuniverse liked this · 2 years ago
shibushiuniverse liked this · 2 years ago -
 lovingeducationsunrisefreak liked this · 3 years ago
lovingeducationsunrisefreak liked this · 3 years ago -
 joliee-petite liked this · 3 years ago
joliee-petite liked this · 3 years ago -
 sleepymr liked this · 3 years ago
sleepymr liked this · 3 years ago -
 kaekingston liked this · 4 years ago
kaekingston liked this · 4 years ago -
 r-dical liked this · 4 years ago
r-dical liked this · 4 years ago -
 lapusia liked this · 4 years ago
lapusia liked this · 4 years ago -
 miisbee liked this · 4 years ago
miisbee liked this · 4 years ago -
 ishtarsdagger reblogged this · 4 years ago
ishtarsdagger reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 mileyflzliam reblogged this · 4 years ago
mileyflzliam reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 emgosnell reblogged this · 4 years ago
emgosnell reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 complementaryxcolors liked this · 4 years ago
complementaryxcolors liked this · 4 years ago -
 spicy-salmon-julien liked this · 4 years ago
spicy-salmon-julien liked this · 4 years ago -
 gonetomoreno liked this · 4 years ago
gonetomoreno liked this · 4 years ago -
 wachsurfer2018 liked this · 4 years ago
wachsurfer2018 liked this · 4 years ago -
 sonofelicediprofessione reblogged this · 5 years ago
sonofelicediprofessione reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 sonofelicediprofessione liked this · 5 years ago
sonofelicediprofessione liked this · 5 years ago -
 hironojp liked this · 5 years ago
hironojp liked this · 5 years ago -
 lexi-late liked this · 5 years ago
lexi-late liked this · 5 years ago -
 megacosms reblogged this · 5 years ago
megacosms reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 straworriez reblogged this · 5 years ago
straworriez reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 tiffanylleto reblogged this · 5 years ago
tiffanylleto reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 moss--moss liked this · 5 years ago
moss--moss liked this · 5 years ago -
 4mockingjay liked this · 5 years ago
4mockingjay liked this · 5 years ago -
 m-faith liked this · 5 years ago
m-faith liked this · 5 years ago -
 the-dreamward liked this · 5 years ago
the-dreamward liked this · 5 years ago -
 rebel-girl-queen-of-my-world liked this · 5 years ago
rebel-girl-queen-of-my-world liked this · 5 years ago -
 schoolnerd3006 liked this · 5 years ago
schoolnerd3006 liked this · 5 years ago -
 katilia4 liked this · 5 years ago
katilia4 liked this · 5 years ago -
 willawitch liked this · 5 years ago
willawitch liked this · 5 years ago -
 abby7598 reblogged this · 5 years ago
abby7598 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 agentlogancatt reblogged this · 5 years ago
agentlogancatt reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 catgirlbossperson liked this · 5 years ago
catgirlbossperson liked this · 5 years ago -
 cryptbirth reblogged this · 5 years ago
cryptbirth reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 hue-d reblogged this · 5 years ago
hue-d reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 spaxey reblogged this · 5 years ago
spaxey reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 spaxey reblogged this · 5 years ago
spaxey reblogged this · 5 years ago