The Infrared Visible Andromeda: This Remarkable Synthetic Color Composite Image Was Assembled From Archives

The Infrared Visible Andromeda: This remarkable synthetic color composite image was assembled from archives of visible light and infrared astronomy image data. The field of view spans the Andromeda Galaxy are also included in the frame. via NASA
js
More Posts from Xnzda and Others
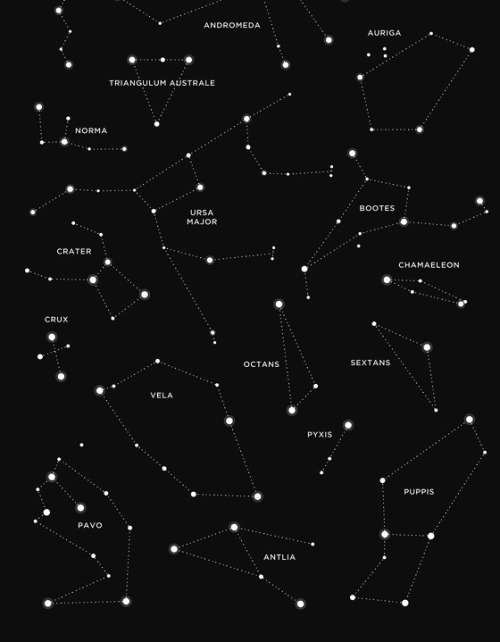
I realized why the idea of constellations has always swayed me. constellations are so very human.
our wonder of the stars is bone-sunk; we’ve been thinking and dreaming and watching and watching and watching since the beginning of time, and we looked for so long that we started making connections.
we played a celestial game of connect-the-dots; trying to find order in something so vast and trying to show that the stars are in everything and everything is in the stars.
we plucked pictures out of the infinite; there’s a dog, there’s a bear, there’s a lion, see? look, right there; the stars hold and mirror back everything we see.
but then it went a step further. instead of everyday things, we stopped picking out the cups and the bears, and instead we saw stories.
look, Andromeda, chained to a rock and waiting to be devoured by Cetus. there’s Orion, and Hercules, and do you see Orpheus’ lyre? Zeus sent an eagle to retrieve it after Orpheus’ death and he placed it in the sky.
we did the most human thing imaginable: we wrote our stories into the stars. we filled the night sky; previously so vast, so unknowable; with our history. we forged connections to the stars and made it so our children will always know where they come from.

Photographer Luc Jamet recently won astronomy photographer of the year for this gorgeous and eerie image of the total solar eclipse seen from the Norwegian territory of Svalbard on March 20, 2015.

The only home we’ve ever known. Clouds and sunlight over the Indian Ocean, as seen from Discovery during the STS-96 mission in 1999.


Astronauts talking about viewing the earth from the moon, from The Overview Effect: Awe and Self-Transcendent Experience in Space Flight
Stellar Winds
Stellar winds are fast moving flows of material (protons, electrons and atoms of heavier metals) that are ejected from stars. These winds are characterised by a continuous outflow of material moving at speeds anywhere between 20 and 2,000 km/s.
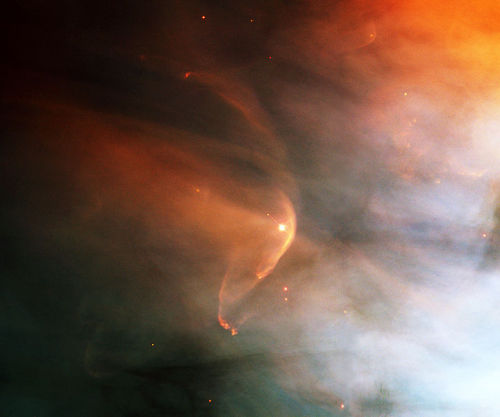

In the case of the Sun, the wind ‘blows’ at a speed of 200 to 300 km/s from quiet regions, and 700 km/s from coronal holes and active regions.
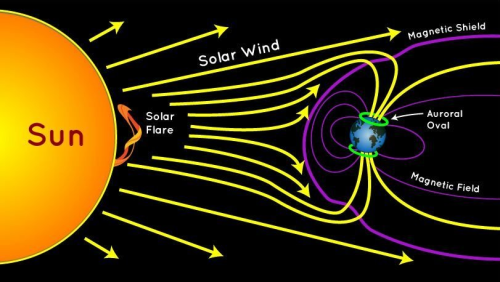
The causes, ejection rates and speeds of stellar winds vary with the mass of the star. In relatively cool, low-mass stars such as the Sun, the wind is caused by the extremely high temperature (millions of degrees Kelvin) of the corona.

his high temperature is thought to be the result of interactions between magnetic fields at the star’s surface, and gives the coronal gas sufficient energy to escape the gravitational attraction of the star as a wind. Stars of this type eject only a tiny fraction of their mass per year as a stellar wind (for example, only 1 part in 1014 of the Sun’s mass is ejected in this way each year), but this still represents losses of millions of tonnes of material each second. Even over their entire lifetime, stars like our Sun lose only a tiny fraction of 1% of their mass through stellar winds.
In contrast, hot, massive stars can produce stellar winds a billion times stronger than those of low-mass stars. Over their short lifetimes, they can eject many solar masses (perhaps up to 50% of their initial mass) of material in the form of 2,000 km/sec winds.

These stellar winds are driven directly by the radiation pressure from photons escaping the star. In some cases, high-mass stars can eject virtually all of their outer envelopes in winds. The result is a Wolf-Rayet star.
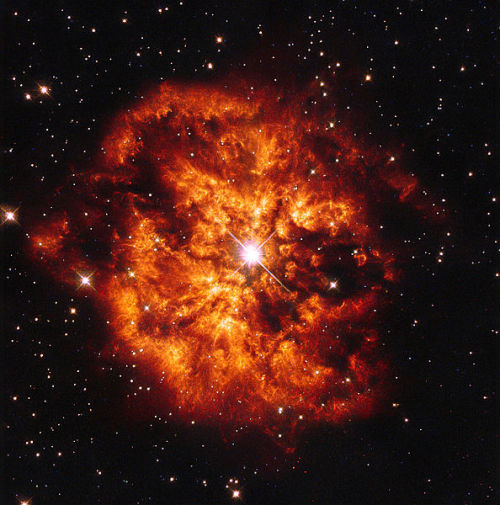

Stellar winds play an important part in the chemical evolution of the Universe, as they carry dust and metals back into the interstellar medium where they will be incorporated into the next generation of stars.
source (read more) + Wolf–Rayet star

lesbians in space

Atmospheric Jellyfish are described as jellyfish-like creature seen floating in the Earth’s atmosphere. Atmospheric Jellyfish are said to look like normal jellyfish except they are floating in the sky much like a cloud and are seen mostly around military bases. Skeptics believe that the Atmospheric Jellyfish could be misidentified clouds or weather balloons however believers hold true to the idea and remember the time that NASA sent 60,000 jellyfish into space during their From Undersea to Outer Space experiment.
-
 tropicaldepressionlea liked this · 1 year ago
tropicaldepressionlea liked this · 1 year ago -
 thisshitisnotbad liked this · 1 year ago
thisshitisnotbad liked this · 1 year ago -
 baddestvenus-in-virgo liked this · 1 year ago
baddestvenus-in-virgo liked this · 1 year ago -
 melancholicposts reblogged this · 1 year ago
melancholicposts reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 whowhatwhyyy liked this · 1 year ago
whowhatwhyyy liked this · 1 year ago -
 theonlymohammmed liked this · 1 year ago
theonlymohammmed liked this · 1 year ago -
 whowhatwhyyy reblogged this · 1 year ago
whowhatwhyyy reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 inether reblogged this · 1 year ago
inether reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 notasaintq reblogged this · 1 year ago
notasaintq reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 nateconnolly liked this · 1 year ago
nateconnolly liked this · 1 year ago -
 jessystardust liked this · 2 years ago
jessystardust liked this · 2 years ago -
 heliomove liked this · 2 years ago
heliomove liked this · 2 years ago -
 yearsfield reblogged this · 2 years ago
yearsfield reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 the-alexander-wolf liked this · 2 years ago
the-alexander-wolf liked this · 2 years ago -
 blackmoonwhitestar liked this · 2 years ago
blackmoonwhitestar liked this · 2 years ago -
 professionalprocrastinator597 liked this · 2 years ago
professionalprocrastinator597 liked this · 2 years ago -
 cal2277 liked this · 3 years ago
cal2277 liked this · 3 years ago -
 gnacorock liked this · 3 years ago
gnacorock liked this · 3 years ago -
 leavejenalone reblogged this · 3 years ago
leavejenalone reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 leavejenalone liked this · 3 years ago
leavejenalone liked this · 3 years ago -
 ihateangelalva reblogged this · 3 years ago
ihateangelalva reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 808pm reblogged this · 3 years ago
808pm reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 ihateangelalva liked this · 3 years ago
ihateangelalva liked this · 3 years ago -
 phuckyodopeblog reblogged this · 3 years ago
phuckyodopeblog reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 phuckyodopeblog liked this · 3 years ago
phuckyodopeblog liked this · 3 years ago -
 alleyesonnme liked this · 3 years ago
alleyesonnme liked this · 3 years ago -
 cebu-in-space reblogged this · 3 years ago
cebu-in-space reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 cebu-in-space liked this · 4 years ago
cebu-in-space liked this · 4 years ago -
 iregretallthis liked this · 4 years ago
iregretallthis liked this · 4 years ago -
 wheresmyfuckingfood liked this · 4 years ago
wheresmyfuckingfood liked this · 4 years ago -
 peachlovesapricot liked this · 4 years ago
peachlovesapricot liked this · 4 years ago -
 muroimasane liked this · 4 years ago
muroimasane liked this · 4 years ago -
 illusionist69s reblogged this · 4 years ago
illusionist69s reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 illusionist69s liked this · 4 years ago
illusionist69s liked this · 4 years ago -
 generouspsychicoafduck liked this · 4 years ago
generouspsychicoafduck liked this · 4 years ago -
 jubaa reblogged this · 4 years ago
jubaa reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 brownnreckless reblogged this · 4 years ago
brownnreckless reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 babyzillion reblogged this · 4 years ago
babyzillion reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 theinfiniteessence liked this · 4 years ago
theinfiniteessence liked this · 4 years ago -
 immajustbeoverhere reblogged this · 4 years ago
immajustbeoverhere reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 immajustbeoverhere liked this · 4 years ago
immajustbeoverhere liked this · 4 years ago