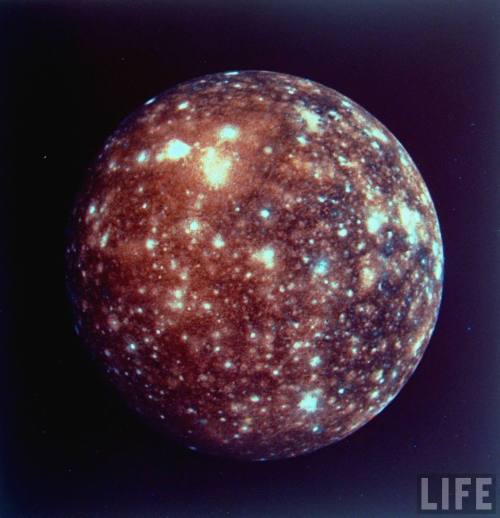
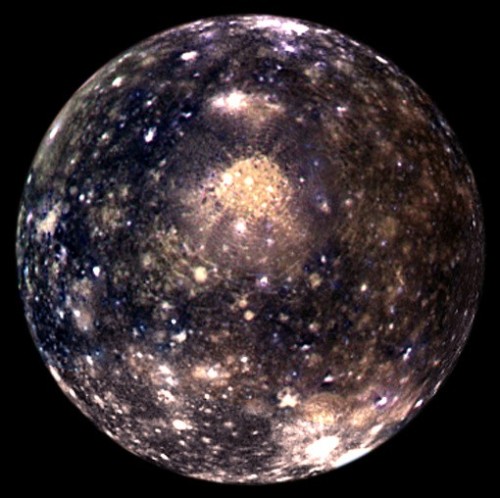
Light From Cygnus A: Celebrating Astronomy In This International Year Of Light, The Detailed Image Reveals
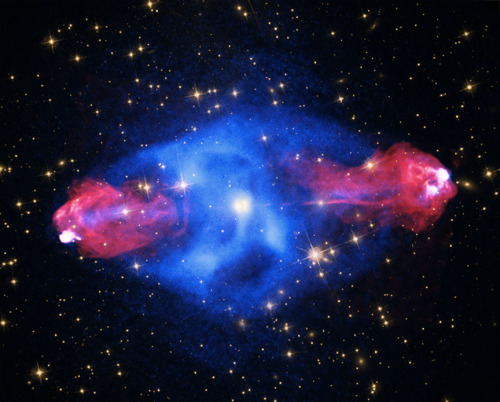

Light from Cygnus A: Celebrating astronomy in this International Year of Light, the detailed image reveals spectacular active galaxy Cygnus A in light across the electromagnetic spectrum. Incorporating X-ray data extends to either side along the same axis for nearly 300,000 light-years powered by jets of relativistic particles emanating from the galaxys central supermassive black hole. Hot spots likely mark the ends of the jets impacting surrounding cool, dense material. Confined to yellow hues, optical wavelength data of the galaxy from Hubble and the surrounding field in the Digital Sky Survey complete a remarkable multiwavelength view. via NASA
js
More Posts from Xnzda and Others
I realized why the idea of constellations has always swayed me. constellations are so very human.
our wonder of the stars is bone-sunk; we’ve been thinking and dreaming and watching and watching and watching since the beginning of time, and we looked for so long that we started making connections.
we played a celestial game of connect-the-dots; trying to find order in something so vast and trying to show that the stars are in everything and everything is in the stars.
we plucked pictures out of the infinite; there’s a dog, there’s a bear, there’s a lion, see? look, right there; the stars hold and mirror back everything we see.
but then it went a step further. instead of everyday things, we stopped picking out the cups and the bears, and instead we saw stories.
look, Andromeda, chained to a rock and waiting to be devoured by Cetus. there’s Orion, and Hercules, and do you see Orpheus’ lyre? Zeus sent an eagle to retrieve it after Orpheus’ death and he placed it in the sky.
we did the most human thing imaginable: we wrote our stories into the stars. we filled the night sky; previously so vast, so unknowable; with our history. we forged connections to the stars and made it so our children will always know where they come from.

HCG 87: A Small Group of Galaxies : Sometimes galaxies form groups. For example, our own Milky Way Galaxy is part of the Local Group of Galaxies. Small, compact groups, like Hickson Compact Group 87 shown above, are interesting partly because they slowly self-destruct. Indeed, the galaxies of HCG 87 are gravitationally stretching each other during their 100-million year orbits around a common center. The pulling creates colliding gas that causes bright bursts of star formation and feeds matter into their active galaxy centers. HCG 87 is composed of a large edge-on spiral galaxy visible near the image center, an elliptical galaxy visible to its right, and a spiral galaxy visible near the top. The small spiral near the center might be far in the distance. Several stars from our Galaxy are also visible in the foreground. Studying groups like HCG 87 allows insight into how all galaxies form and evolve. via NASA
js

A cosmic blossom
IC 5148 is a beautiful planetary nebula located some 3000 light-years away in the constellation of Grus (The Crane). The nebula has a diameter of a couple of light-years, and it is still growing at over 50 kilometres per second — one of the fastest expanding planetary nebulae known. The term “planetary nebula” arose in the 19th century, when the first observations of such objects — through the small telescopes available at the time — looked somewhat like giant planets. Although the name stuck, it represents the expanding shell of gas ejected from old red giant stars late in their lives.
And now this one resembles a lovely blossom with layered petals.
Credit: European Southern Observatory
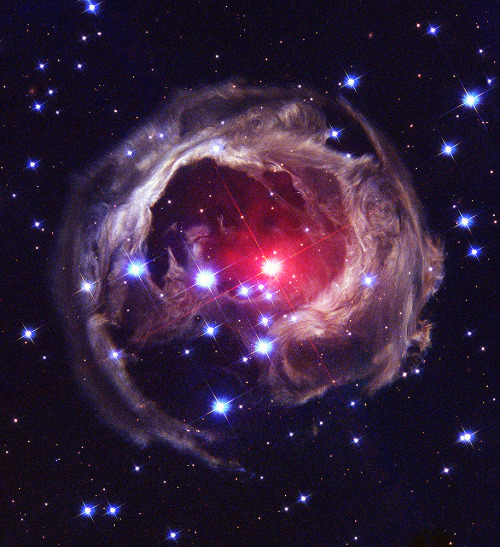

Light Echoes from V838 Mon
For reasons unknown, star V838 Mon’s outer surface suddenly greatly expanded with the result that it became the brightest star in the entire Milky Way Galaxy in January 2002. Then, just as suddenly, it faded. A stellar flash like this has never been seen before.
It’s true that supernovae and novae expel matter out into space. But while the V838 Mon flash appears to expel material into space, what is seen here is actually an outwardly moving light echo of the bright flash. In a light echo, light from the flash is reflected by successively more distant rings in the ambient interstellar dust that already surrounded the star.
V838 Mon lies about 20,000 light years away toward the constellation of Monoceros the unicorn. In this Hubble Space Telescope image from February 2004, the light echo is about six light years in diameter.
Image Credit: NASA, APOD, ESA, H. E. Bond (STScI)

stars, mercury, and solar corona, photographed by stereo a, january 2009.
27 frames, photographed over 36 hours, 2nd-3rd january. the sun is out of frame right.
image credit: nasa/stereo. animation: ageofdestruction.
-
 gimmehope liked this · 5 months ago
gimmehope liked this · 5 months ago -
 scarsglowing-windy liked this · 6 years ago
scarsglowing-windy liked this · 6 years ago -
 scarsglowing-windy reblogged this · 6 years ago
scarsglowing-windy reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 demmimontoyaa reblogged this · 6 years ago
demmimontoyaa reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 xnzda reblogged this · 6 years ago
xnzda reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 brotosstm liked this · 6 years ago
brotosstm liked this · 6 years ago -
 fireburnslovely liked this · 7 years ago
fireburnslovely liked this · 7 years ago -
 sarcasm-tea reblogged this · 7 years ago
sarcasm-tea reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 ineedspacex-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
ineedspacex-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 passion-images liked this · 9 years ago
passion-images liked this · 9 years ago -
 teenxhippie-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
teenxhippie-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 theufos51 liked this · 9 years ago
theufos51 liked this · 9 years ago -
 herkidalpaca reblogged this · 9 years ago
herkidalpaca reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 herkidalpaca liked this · 9 years ago
herkidalpaca liked this · 9 years ago -
 superspacenerdblog liked this · 9 years ago
superspacenerdblog liked this · 9 years ago -
 beastboy826 liked this · 9 years ago
beastboy826 liked this · 9 years ago -
 nealieeee liked this · 9 years ago
nealieeee liked this · 9 years ago -
 cat20sblog reblogged this · 9 years ago
cat20sblog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 cat20sblog liked this · 9 years ago
cat20sblog liked this · 9 years ago -
 xx119999-blog liked this · 9 years ago
xx119999-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 girlgetagrip-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
girlgetagrip-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 girlgetagrip-blog liked this · 9 years ago
girlgetagrip-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 mini-space-alien-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
mini-space-alien-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 standupsinghellalujah-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
standupsinghellalujah-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 my-heart-keeps-giving-in reblogged this · 9 years ago
my-heart-keeps-giving-in reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 annabananaphone liked this · 9 years ago
annabananaphone liked this · 9 years ago -
 annabananaphone reblogged this · 9 years ago
annabananaphone reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 lonerstonerchick69 liked this · 9 years ago
lonerstonerchick69 liked this · 9 years ago -
 octobersky reblogged this · 9 years ago
octobersky reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 getupoffonit liked this · 9 years ago
getupoffonit liked this · 9 years ago -
 asvpkta liked this · 9 years ago
asvpkta liked this · 9 years ago -
 emeraldorchard liked this · 9 years ago
emeraldorchard liked this · 9 years ago -
 captainzazzle-blog liked this · 9 years ago
captainzazzle-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 fenixed reblogged this · 9 years ago
fenixed reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 ibnbanuamela reblogged this · 9 years ago
ibnbanuamela reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 all-the-space reblogged this · 9 years ago
all-the-space reblogged this · 9 years ago