Our Planet: 8 Stunning Views Of Earth From Space
Our Planet: 8 Stunning Views of Earth from Space
Swirling clouds, deep blue oceans and textured land- and icescapes are among the many faces of our planet revealed in NASA’s new photo-essay book: Earth. This collection of 69 images captured by satellites tells a story of a 4.5-billion-year-old planet where there is always something new to see. Earth is a beautiful, awe-inspiring place, and it is the only world most of us will ever know. It is your planet. It is NASA’s mission. The book is available now in hardcover and ebook, and online with interactive features.
Here are eight of those breathtaking images for your viewing pleasure.
Channel Country, Australia

These wide floodplains in Queensland, Australia are unique on the planet. Scientists think they are caused by the extreme variation in water and sediment discharges from the rivers. In many years there is no rainfall at all, and the rivers are effectively non-existent. In years of modest rainfall, the main channels will carry some water, sometimes spilling over into narrow water holes known as billabongs.
Every few decades, the floodplain carries extremely high discharges of water. For instance, tropical storms to the north can lead to great water flows that inundate the entire width of the floodplain. On such occasions, the floodplain appears as series of brown and green water surfaces with only tree tops indicating the location of the islands. Such is the case in this image taken from the International Space Station in September 2016.
Grounded in the Caspian, Kazakhstan

A wide variety of ice forms in the Caspian Sea, which stretches from Kazakhstan to Iran. Just offshore, a well-developed expanse of consolidated ice appears bright white. Farther offshore, a gray-white field of chunky, hummocked ice has detached and is slowly drifting around a polynya, an area of open water surrounded by sea ice. That darker patch is actually growing young, thin ice and nilas, a term that designates sea ice crust up to 10 centimeters (4 inches) in thickness.
The close-up shows nilas and a white, diamond-shaped piece of ice. It might look like this chunk is on the move, cutting a path through thinner ice. But it’s more likely that the “diamond” was stuck to the sea bottom and the wind pushed ice around it.
Tsauchab River Bed, Namibia

The Tsauchab River is a famous landmark for the people of Namibia and tourists. Yet few people have ever seen the river flowing with water. In December 2009, an astronaut on the International Space Station caught this glimpse of the Tsauchab River bed jutting into the sea of red dunes. It ends in a series of light-colored, silty mud holes on the dry lake floor.
Like several other rivers around the Namib Desert, the Tsauchab brings sediment down from the hinterland toward the coastal lowland. This sediment is then blown from the river beds, and over tens of millions of years it has accumulated as the red dunes of the Namib Sand Sea.
Taranaki and Egmont, New Zealand

The circular pattern of New Zealand’s Egmont National Park stands out from space as a human fingerprint on the landscape. The park protects the forested and snow-capped slopes around Mount Taranaki (Mount Egmont to British settlers). It was established in 1900, when officials drew a radius of 10 kilometers around the volcanic peak. The colors differentiate the protected forest (dark green) from once-forested pasturelands (light- and brown-green).
Named by the native Maori people, Taranaki stands 2,518 meters (8,260 feet) tall, and it is one of the world’s most symmetric volcanoes. It first became active about 135,000 years ago. By dating lava flows, geologists have figured out that small eruptions occur roughly every 90 years and major eruptions every 500 years. Landsat 8 acquired this image of Taranaki and the park in July 2014.
Storms Stir Up Sediment in Bermuda

In October 2014, the eye of Hurricane Gonzalo passed right over Bermuda. In the process, the potent storm stirred up the sediments in the shallow bays and lagoons around the island, spreading a huge mass of sediment across the North Atlantic Ocean. This Landsat 8 image shows the area after Gonzalo passed through.
The suspended sediments were likely a combination of beach sand and carbonate sediments from around the shallows and reefs. Coral reefs can produce large amounts of calcium carbonate, which stays on the reef flats (where there are coralline algae that also produce carbonate) and builds up over time to form islands.
Framing an Iceberg in the South Atlantic Ocean

In June 2016, the Suomi NPP satellite captured this image of various cloud formations in the South Atlantic Ocean. Note how low stratus clouds framed a hole over iceberg A-56 as it drifted across the sea.
The exact reason for the hole in the clouds is somewhat of a mystery. It could have formed by chance, although imagery from the days before and after this date suggest something else was at work. It could be that the relatively unobstructed path of the clouds over the ocean surface was interrupted by thermal instability created by the iceberg. In other words, if an obstacle is big enough, it can divert the low-level atmospheric flow of air around it, a phenomenon often caused by islands.
Lofted Over Land in Madagascar

Along the muddy Mania River, midday clouds form over the forested land but not the water. In the tropical rainforests of Madagascar, there is ample moisture for cloud formation. Sunlight heats the land all day, warming that moist air and causing it to rise high into the atmosphere until it cools and condenses into water droplets. Clouds generally form where air is ascending (over land in this case), but not where it is descending (over the river). Landsat 8 acquired this image in January 2015.
A Lava Lamp Look at the Atlantic Ocean

Stretching from tropical Florida to the doorstep of Europe, the Gulf Stream carries a lot of heat, salt, and history. This river of water is an important part of the global ocean conveyor belt, moving water and heat from the Equator toward the far North Atlantic. It is one of the strongest currents on Earth and one of the most studied. Its discovery is often attributed to Benjamin Franklin, though sailors likely knew about the current long before they had a name for it.
This image shows a small portion of the Gulf Stream off of South Carolina as it appeared in infrared data collected by the Landsat 8 satellite in April 2013. Colors represent the energy—heat—being emitted by the water, with cooler temperatures in purple and the warmest water being nearly white. Note how the Gulf Stream is not a uniform band but instead has finer streams and pockets of warmer and colder water.
These images are just a few from our new book called Earth. Explore the other 61 images here.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nauticastro and Others

The rings of Saturn, observed by Voyager 2 on this day in 1981.

When it comes to the Moon, everyone wants the same things. Not in the sense of having shared goals, but in the sense that all players target the same strategic sites—state agencies and the private sector alike. That’s because, whether you want to do science or make money, you will need things such as water and light.






— Laura Gilpin, The Hocus-Pocus of the Universe (1977)

From Earthrise to the black hole: astronomy’s most famous images.
Photographs from history that capture humanity’s exploration of the heavens.

20 July 1969
One of the most iconic views of Earth, taken from the Apollo 11 spacecraft as it orbited the moon. Describing the scene, the astronaut Neil Armstrong said: ‘It suddenly struck me that that tiny pea, pretty and blue, was the Earth. I put up my thumb and shut one eye, and my thumb blotted out the planet Earth. I didn’t feel like a giant. I felt very, very small’ | This caption was updated on 11 April 2019 to correct the date the picture was taken, photograph: Nasa.

21 July 1969
Buzz Aldrin, the lunar module pilot for the first moon landing, poses on the lunar surface. The footprints of the astronauts are clearly visible in the soil. Neil Armstrong took the picture with a 70mm Hasselblad lunar surface camera Photograph: American Photo Archive/Alamy

25 February 1979
This dramatic view of Jupiter’s great red spot and its surroundings was obtained by the Voyager 1 space probe
Photograph: JPL/Nasa/UIG/Getty Images

14 February 1990
Often referred to as ‘the pale blue dot’ image, this picture was taken when Voyager 1 was 4bn miles (6.4bn km) from Earth and 32 degrees above the ecliptic plane. Earth is a mere point of light, just 0.12 pixels in size when viewed from that distance. The fuzzy light is scattered sunlight because Earth was close to the sun (from the perspective of Voyager)
Photograph: JPL/Nasa

6 January 2004
The first colour image of Mars taken by the panoramic camera on the Mars Exploration Rover Spirit. It was the sharpest photograph ever taken on the surface of the planet
Photograph: JPL/Nasa/AP

25 September 2012
Called the eXtreme Deep Field, or XDF, this photo was assembled by combining 10 years of Hubble space telescope photographs taken of a patch of sky at the centre of the original Hubble Ultra Deep Field. By collecting faint light over many hours of observation, the telescope revealed thousands of galaxies, both nearby and very distant, making it the deepest image of the universe ever taken at that time
Photograph: Hubble space telescope/Nasa/ESA

24 July 2015
A combination of images captured by the New Horizons space probe, with enhanced colours to show differences in the composition and texture of Pluto’s surface
Photograph: AP

10 April 2019
The first image of a black hole, captured by the Event Horizon telescope (EHT) – a planet-scale array of eight ground-based radio telescopes forged through international collaboration. The shadow of a black hole seen here is the closest we can come to an image of the black hole itself, a completely dark object from which light cannot escape
Photograph: EHT Collaboration/UCL

First picture from Israeli spacecraft Beresheet at nearly 38,000 km from Earth by The-Internet-Sir
★☆★ SPACE ★☆★

comme the stars perfume
I drew a little something for the Hiveworks micro comic summer~



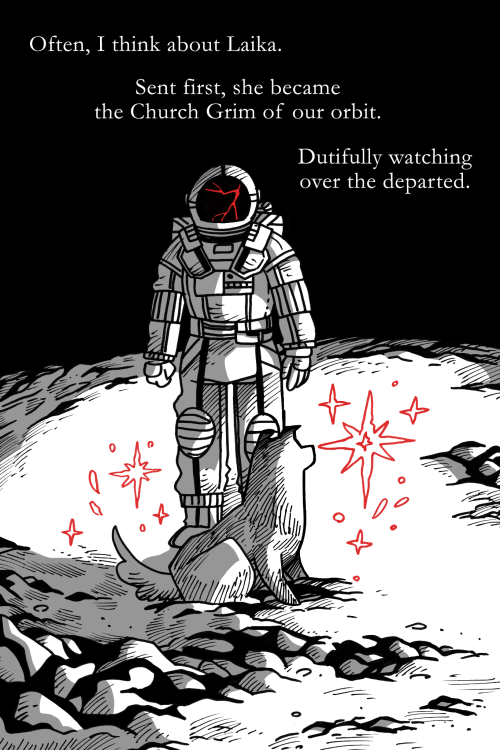

-
 worthsertaimutan liked this · 1 year ago
worthsertaimutan liked this · 1 year ago -
 lola1695 liked this · 2 years ago
lola1695 liked this · 2 years ago -
 faunafloraflight reblogged this · 2 years ago
faunafloraflight reblogged this · 2 years ago -
 gnsispr liked this · 4 years ago
gnsispr liked this · 4 years ago -
 hopefuldreamers-world liked this · 4 years ago
hopefuldreamers-world liked this · 4 years ago -
 hushedwildtales reblogged this · 4 years ago
hushedwildtales reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 mystical-mushroom liked this · 5 years ago
mystical-mushroom liked this · 5 years ago -
 saltyhollywoodreaderskeleton reblogged this · 5 years ago
saltyhollywoodreaderskeleton reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 treknstuff reblogged this · 5 years ago
treknstuff reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 treknstuff liked this · 5 years ago
treknstuff liked this · 5 years ago -
 skywalker-anakin reblogged this · 5 years ago
skywalker-anakin reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 snesbaby liked this · 5 years ago
snesbaby liked this · 5 years ago -
 poemforthesmallthings reblogged this · 5 years ago
poemforthesmallthings reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 pandapops123 reblogged this · 5 years ago
pandapops123 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ludmila199 liked this · 5 years ago
ludmila199 liked this · 5 years ago -
 make-like-a-tree-and-leaf reblogged this · 5 years ago
make-like-a-tree-and-leaf reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ikasdu64 liked this · 5 years ago
ikasdu64 liked this · 5 years ago -
 polskza liked this · 5 years ago
polskza liked this · 5 years ago -
 bfsewoon reblogged this · 5 years ago
bfsewoon reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 nahundfern reblogged this · 5 years ago
nahundfern reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 hardlykedi reblogged this · 5 years ago
hardlykedi reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 bucketodoom reblogged this · 5 years ago
bucketodoom reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 peripeteia-denouement reblogged this · 5 years ago
peripeteia-denouement reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 lazyfanphilosopher liked this · 5 years ago
lazyfanphilosopher liked this · 5 years ago -
 drunkenpeanut reblogged this · 5 years ago
drunkenpeanut reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 shadowedseas reblogged this · 5 years ago
shadowedseas reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 worktype reblogged this · 5 years ago
worktype reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 nauticastro reblogged this · 5 years ago
nauticastro reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 larkhive reblogged this · 5 years ago
larkhive reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 thesassygirl1 liked this · 6 years ago
thesassygirl1 liked this · 6 years ago -
 spacesquidposting reblogged this · 6 years ago
spacesquidposting reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 emmrakul liked this · 6 years ago
emmrakul liked this · 6 years ago -
 reallygrandkitten reblogged this · 6 years ago
reallygrandkitten reblogged this · 6 years ago

