I Jotted Down For A Friend Of Mine Some Tips And Notes On How I Approach Drawing Hair, And Things I Keep



I jotted down for a friend of mine some tips and notes on how I approach drawing hair, and things I keep in mind while doing so, and thought I’d share. There are loads of other ways to do it, and the learning never stops, so I hope this helps!
More Posts from Nastysynth and Others
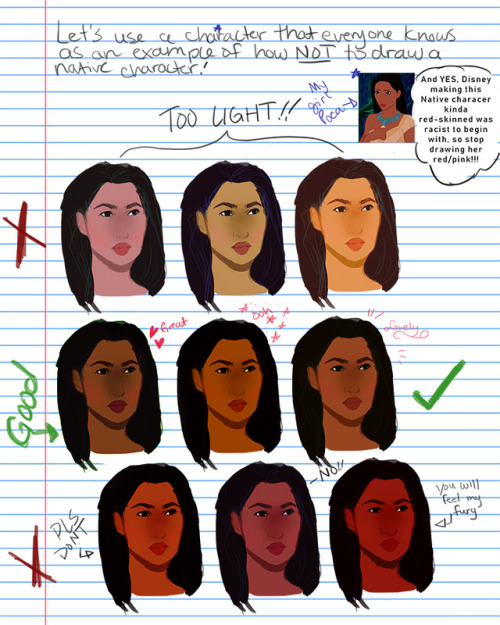






How I draw skin Part 2: DON”T DRAW NATIVE PEOPLE WITH RED SKIN!!!! A tutorial
For the first tutorial on how I draw skin, see the post here.
But seriously, I’ve seen too many drawings of Native characters with literal red/pink skin to count so just in case some of you are having troubles with drawing Native people, I’ve provided a guide for you. Please take my swatches if it helps!! and no more red skinned people, please <0<
Disclaimer: this tutorial is mainly about the artistic depictions of Indigenous Peoples in North America, where the slur and redskin caricature originated, but it would still be racist to draw other non-North/Central/South American Indigenous groups like this so…..don’t.







i wanted to update my VERY OLD nose tutorial now that ive learned how to draw! as always, this isn’t an all encompassing guide– just a jumping off point for practice@
LITERALLY the most Lynch thing i’ve seen








some puppies studies ( ͡° ͜ʖ ͡°) 🐶 | Instagram
(Edited) + more studies lkdafña
When doing full body sketches do you use shapes for different body parts? (I.e triangles for the torso, circles for the face, etc.) If so, could you show us how one could use said shapes to get their anatomy right? Thanks!
lucky you, my latest figure drawings have just been posted so i feel like i can use them for my explanation here!!









above all: THINK IN THREE DIMENSIONS, NOT JUST FLAT SHAPES. THE CONTURE/ANGLE IS VERY IMPORTANT!! THE RIB CAGE WITH SHOW THE ANGLE UR BODY IS AT THE MOST!!
I have two questions! First: have you ever thought of doing a tarot card suit for your characters? I think it'd work really well for them! And two: help me how do I draw legs
@gravitality
Hi!! I’ve absolutely been thinking about that, yeah, in fact I recently talked about that to my boyfriend just recently. It’ll likely happen after october! And to answer your second question! I made a thing on legs that i hope you’ll find useful!!
So. I’ve already explained basics on legs here, but I don’t think it hurts to go through some extra details to help you understand legs some more.

The very basic thing is to imagine legs as teardrops. Again, this has already been covered in said tutorial above, but I figured it’s still good to mention even the most basic thing that I know of. I still highly recommend you check it out to get in more detail and to see some other examples and practices that you do. But basically, think of legs in the shapes of teardrops, when it comes to shape. If you need a simple stick-figure to connect the legs in the first place, make sure that they bend at the knees a bit so that the legs don’t come off as stiff and unnatural.

As you can see, this method works perfectly for realistic legs as it does for stylistic ones. Remember to use these as a guideline, never to be the exact base of the legs you will be drawing. If you draw traditionally, remember not to draw these guides too hard, or they will be hard to erase/do freestyle!

But how do you actually draw out the legs without drawing them perfectly straight, as shown to the left? The trick is to add volume to them, and how you do that can be winged to your own liking. The idea is to think in curves. As no leg is perfectly straight. You may make these curves minimal if you don’t want them to be curvy, but keep in mind, still, that not even your own bones are perfectly straight, so it is highly recommended that you make them bend, at least a little.

It all depends on how you draw them as well. Say you put your legs together, as shown in this picture, what happens to the fat and muscle? Naturally, they press together, much like how thighs squish on the surface when you sit down (I’m sure most people know what I’m talking about). Make sure this shows in your art! This is very important to keep in mind, because it makes it all look more natural and believable. Try to cross your legs or stand up and sit down again for real-life examples!


The same applies for stretching your legs, more or less, except they appear to become more ‘hollow’ and slimmer. They become less soft to the touch, too, and might show. Try stretching your legs and feel where the muscles tense and where it feels ‘hollow’. This is very helpful with your art.

Many leg tutorials talk about legs without mentioning the behind. It requires a tutorial on it’s own, in all honesty, but this is the most simplest way to draw it connecting to the legs. Remember that it comes in many different shapes, and this is just a super basic guide! Two circles overlapping, while following the line and flow of the legs. Remember the muscle/fat as mentioned above!

Okay, so we got the basics of leg shapes figured out? What if you want o draw them in a certain pose, or with a certain silhouette, but perhaps do not have the reference for it? Or you want to blend your style into it? The key is to not shy away from doodling the form. Make mess, draw lightly and don’t care about the anatomy. That way you’ll get everything down without it appearing stiff. You can clean up the sketch later, always, and if you can, use a reference after you have drawn your pose, to correct your drawing.

Remember that the hips do a lot to the pose of the legs! Make sure they are in flow with your legs, so that it can look more natural. Remembers that hips ‘rotate’ with the spine.

I’ve talked about this method before when it comes to posing, and the same applies for the legs. One way to make legs appear ‘steady’ is to picture them standing in a line, and one of those legs need not to stray from the lines too much, making it steady. If you want a dynamic pose despite the steady pose, you can always have the other leg stray from the line, since it only matters that one leg is steady. This method can create good, casual poses without making them appear boring. (also notice how the teardrop shapes are used here, despite the highly stylized legs)

Do you want a highly dynamic pose, or them to appear unsteady, then skip the line entirely and make both legs aim away from it completely. As you can see, the legs appear more moving, in action, as if they’re fighting, falling, or dancing. As you can imagine, this is not a pose that one could stay steady on, suggesting that it’s taken mid-movement. More about posing and this ‘line’ method is talked about in this tutorial.
Hope this helped you, if you have any questions let me know, and if you’d like to check out all my tutorials they can be found here!
I know you probably get these asks a lot, but I've really been trying to try drawing comic pages. I really admire how free and flowing your style is! I've seen your little tutorials and tips and idk what's wrong but I just can't seem to wrap my head around panel composition? Like I do wonderful painting comps, but I can't seem to break out. Do you have any resources or help to get started?
thank you very much!!!!! im just using this ask as an excuse to draw random comic tips i hope thats okay and that you’ll get something out of it
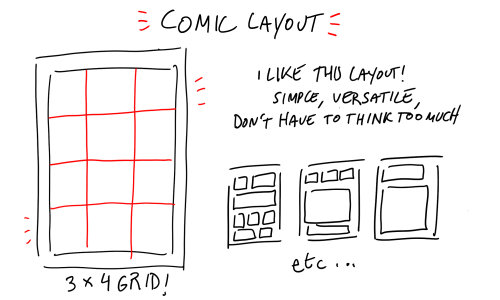

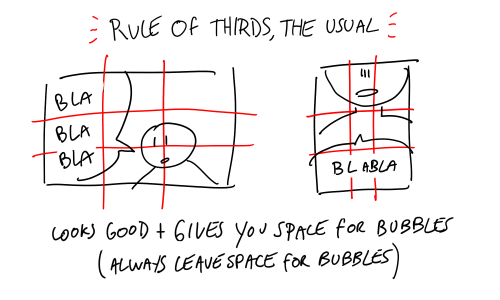



did that help…

Wake up while we still have a chance.
About Yarovit-Yarilo

Today I present you my translation of fragments of two polish academic publications that are great favorites of mine. Fragments chosen are centered around Yarovit and Yarilo. My own comments will be indicated by a „trans. note” disclaimer. The fragments below are merely a part of larger text. I apologize for any context lost to the lack of broader perspective on the whole of the publication.
Mitologia Słowian by Aleksander Gieysztor
Chapter V: Principal deities and myths
Subchapter: „Perun’s many ways - Sventovit, Ruyevit & company, Yarovit-Yarilo”
Yarovit-Yarilo
A deity called Yarovit (trans. note: Herovith, Gerovit, pl: Jarowit) was worshipped in two locations settled by polabian Slavs - in pomeranian Wolgast and in Havelberg, a gord inhabited by the Brizans tribe (pl: Brzeżanie). During the mission of bambergian bishop Otton in Wolgost in 1128 one of his priests hid from an angry crowd in a pagan temple, and there found a giant shield covered in golden plates, that was considered untouchable and would only be carried out during war time, as a blessing of good luck. The preacher snatched the sacred shield and ran back out of the temple terrifying the pursuing crowd - in the sput of the moment they thought they see Yarovit himself. One of the writers compares him to Mars, another calls him the god of war - there is no doubt Yarovit was a martial god. It’s hard to tell if there was any statue in his temple, as the escaping priest only noticed the shield. A shield is a ritual object in many martial cults, for example in roman Regia (trans. note: royal house on the ancient Forum Romanum) a most sacred shield was watched over by guards. So called „Stone of Yarovit” in St. Peter’s church of Wolgast (trans. note: Wolgast is now located in the northeast corner of Germany) is a tombstone dating to the earliest christian times. One of the polabian villagers saw Yarovit appear to him „in the robes of his idol” to warn him about the coming missionaries - so there seems to have existed some idol/statue of him (trans. note: episode from Vita s. Ottonis III by Ebonis).
There are no doubts as to the origin of this deity’s name. It came from the root jar-, jaro- meaning strength or severity, but also conveying the idea of stregth coming from youth, as in slavic word „jar” meaning spring. Similar military competences and analogical anatomy of the names strongly connect Yarovit and Sventovit (pl: Świętowit) with one another and with Perun - the supreme warrior god. We could try to follow Ivanov and Toporov (trans. note: famous russian folklorists) in their attempts to strengthen this thesis by means of analysing folklore and comparative religious studies. The baseline for all scholars here is belarusian text from 1846 describing Yarilo as a young man in white robes, barefoot, with human head under his right arm and stalks of rye in his left hand, in a herbal wreath, on a white horse. A ritual, which took place on 27th of April, to welcome spring before the first plowing, was performed by a procession of young girls, one of them dressed as Jarilo, sitting on a white horse, the others singing to her
„Yarilo wandered all over the world / Rye grew high in the fields, he gave women children / And where he set his foot/ There a stack of rye / Where he’s in the grain/ There the stalks grow tall”
Along Yarovit and Yarilo there is also a third name entangled in the cult practices, „Yarun” (pl: Jarun), a ruthenian idol named in Laurentian Codex, as well as a collection of common slavic words, ruthenian „jarovoj” - „of spring” „vernal”; polish word „jare” used to describe grains planted in the spring (trans. note: as opposed to „ozime” grains growing over the winter), ruthenian and czech word for spring „jar”.
As much as we can question the date and quality of this belarusian text it’s undeniable that there is an archaic note ringing in those beliefs - white robes and white horse, flowers and rye stalks, the head held by a victorious rider, the barefoot man, touching the earth with his feet in a cultically significant way, making grain sprout wherever he steps, opening the fields in the spring, with his name, the surveying of the fields. He has been accepted, his traits amalgamated with those of St. George (Sveti Jurij) who is celebrated in some places on 23rd of April (trans. note: julian, not gregorian), accompanied by burning of female effigy called Marena/Marzanna, personifying winter or death, a harbinger of spring. Sometimes young Yarilo is juxtaposed with the old Yarilo, who gives up his place - perhaps loses it in a fight with his young rival.
We can see a bit of a duality shaping up in the image of Yarovit-Yarilo-Yaruna. On one hand he is a warrior, on another an overseer of agricultural activity, which, despite Ivanovs and Toporov’s opinions, doesn’t take any odd naturalistic interpretations on the part of the people as it naturally belongs to the dominion of supreme deities - even Jupiter comes down to bless the roman farmer during his spring festival Vinalii, that falls on… 23rd April.
We also need to examine the toponimastic evidence: the city of Jarilovo and no less than four settlements called Jarilovic in the area od Novogrod the Great. In 18th century diocese of Voronezh festivities were held around an idol called Yarilo from Wednesday to Friday or Saturday in the week after Green Week, as late as 1673 a man would lead the festival, adorned with flowers and bells, with his face painted red and white.
Religia Słowian by Andrzej Szyjewski
Chapter V: The Lost Gods
Subchapter: „Deities of fertility and vegetation”, fragments
We can see the solar hero association even more prominently in Yarovit, worshipped in Wolgast and Havelberg. His very name „Yarovit”, „The Young Victor” is connected to spring, youthful strenght and sexual passion (as in slavic words „jar” - spring, „jurny” - virile, manly, or the phrase „stary ale jary” meaning something along the lines of „old but tough”). This particular god watched over the fertility of fields and forests, humans and beasts - or so we can guess from the threats of Yarovit’s priest made against all those who will choose the „german god” (trans. note: abrahamic god) over their local deity. In Wolgast a sacred golden shield of Jarowit was held described as „great of size and exquisitely made”, a clear solar symbol, that nobody but the god or his priest could touch. As the greatest sanctity in the temple to the polabians it was also a symbol of victory - let’s not forget that Otto of Bamberg describes Yarovit as a war god similar to Mars. As the greatest, untouchable sacred object, and at the same time the harbinger of victory it corresponds fully in its symbolism to the white horse of Sventovit. In the „Vita s. Ottonis” we find a clear reference to Yarovit as the god of military, his name is translated into latin as „Mars” („deo suo Gerovito, qui lingua Latina Mars dictur). Just like with Sventovit we see a trio of interconnected associations: fertility - solar hero - war.
The celebrations of Yarilo mentioned by the missionaries of Otto were likely the planting festival of 15th April. It could involve the god’s „descent” among the people, enacted with the help of the sacred shield. That the god spoke through the lips of żerca (slavic priest) we know from other versions of „Vita s. Ottonis” (trans. note: hagiographic writings about Saint Otto). Scholars try to reconstruct the pre-christian celebrations through XVIII century ethnographic materials concerning Yarilo (admittedly not Yarovit), with ruthenian and belarusian origins. Texts recovered from diocese of Voronezh mention local bishop putting an end to the festivities surrounding Yarilo held on 23rd April in julian calendar (15th of April corresponds in gregorian). In christian context Yarilo is replaced by Saint Jurij (description of the same ritual as one described above follows, girl dressed up as Yarilo, the same song). People would dance circle dances (korovod) on top of the freshly planted fields and end the day with a feast with orgiastic elements. The purpose of the rituals was to close the winter and open the spring; Yarilo opens the gates of earth, letting the spring out.
Yarilo’s attributes clearly point to his role as god of vegetation and fertility. The girl assuming his likeness during the festival, also known as Wiosnołka or Wiesnowka (trans. notes: pronounciation „vyos-NOHW-kah” or „vyes-NOHV-kah”) could be an echo of „divine bride”, an offering to the god, an incentive to arrive with the spring. Many songs refer to Yarilo causing the earth to sprout and bloom as he walks but also summoning dancing girls to him. Circle dances, white robes, white horse and the cut off head are all elements of solar symbolism. The head belongs to Old Yarilo, dethorned and overpowered by his young son. All over the world similar symbols exist - from celtic Curoi to mayan Hunahpu. Young Yarilo matures and dies as the harvest unfolds, then at the end of summer a funeral is held - this time main roles were played by young married women not maidens. They made an effigy of Yarilo (putting some extra effort into shaping his reproductive organs) that they called Kostrub („COST-roob”) and then they put him into his grave, in the ground since in the earth the sun loses it’s powers and dies, letting the new sun take over. The people would sing and cry out about Yarilo dying and ask him to get back on his horse in his golden saddle. Attempts to reconstruct the rituals seem to show that young Jarilo on white horse was juxtaposed with old Yarilo on black goat. Southern slavs practice similar rituals of burning old Badniak (a piece of wood with forked roots) on Christmas Eve to make place for young Božič (son of god). Western Slavs don’t have a deity corresponding to Yarilo - they close the winter in rituals involving Marena/Marzanna, followed by a procession carrying around „maik” or „nowe lato” symbolized by the peak of an evergreen coniferous tree or a rooster as a solar bird.
The Slavs were an agricultural society so agrarian deities were their primary source of relations with divine, cosmic forces. There is a certain myth/archetype that is characteristic for early farmers, the myth of creative murder, in which the first birth, growth and harvest are prompted by the first death - death of a deity, hero, ancestor, who dies sacrificing himself for the people, and from his body the first plants spring, allowing the people to survive. That myth, encated in many cultures in many ways leads to the cincept of a solar god that dies and is reborn cyclically, whose individual fate is reflected by the cycle of growing grain. The stalks loose their heads under the sickles for people to be able to feed. Yarilo (and maybe even Yarovit) makes identical sacrifice.
Art: Jaruna by Ada Konieczna
-
 coyfoxes reblogged this · 1 month ago
coyfoxes reblogged this · 1 month ago -
 gaigun667 liked this · 1 month ago
gaigun667 liked this · 1 month ago -
 anakinskywalkerisfave reblogged this · 8 months ago
anakinskywalkerisfave reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 hearmeout---explosivediarrhea liked this · 8 months ago
hearmeout---explosivediarrhea liked this · 8 months ago -
 crowbartender reblogged this · 9 months ago
crowbartender reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 evilswag liked this · 9 months ago
evilswag liked this · 9 months ago -
 dianemozart reblogged this · 9 months ago
dianemozart reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 dianemozart liked this · 9 months ago
dianemozart liked this · 9 months ago -
 nothingkindafits reblogged this · 9 months ago
nothingkindafits reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 bmoon13 liked this · 10 months ago
bmoon13 liked this · 10 months ago -
 malvo-ish reblogged this · 10 months ago
malvo-ish reblogged this · 10 months ago -
 darkblazetriumph liked this · 10 months ago
darkblazetriumph liked this · 10 months ago -
 artking-4 reblogged this · 11 months ago
artking-4 reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 artking-4 reblogged this · 11 months ago
artking-4 reblogged this · 11 months ago -
 spaghetticat3899 reblogged this · 1 year ago
spaghetticat3899 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 spaghetticat3899 liked this · 1 year ago
spaghetticat3899 liked this · 1 year ago -
 artreferencesarchive reblogged this · 1 year ago
artreferencesarchive reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 wittywhit liked this · 1 year ago
wittywhit liked this · 1 year ago -
 aridotdash reblogged this · 1 year ago
aridotdash reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 aridotdash liked this · 1 year ago
aridotdash liked this · 1 year ago -
 manicdragon liked this · 1 year ago
manicdragon liked this · 1 year ago -
 big1ron liked this · 1 year ago
big1ron liked this · 1 year ago -
 fiireflyfields liked this · 1 year ago
fiireflyfields liked this · 1 year ago -
 leos-spot liked this · 1 year ago
leos-spot liked this · 1 year ago -
 jgvfhl reblogged this · 1 year ago
jgvfhl reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 jgvfhl liked this · 1 year ago
jgvfhl liked this · 1 year ago -
 0-starlightstories-0 liked this · 1 year ago
0-starlightstories-0 liked this · 1 year ago -
 tyshazo reblogged this · 1 year ago
tyshazo reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 tyshazo liked this · 1 year ago
tyshazo liked this · 1 year ago -
 booitsloki liked this · 1 year ago
booitsloki liked this · 1 year ago -
 mrfandomwars reblogged this · 1 year ago
mrfandomwars reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 hoshi959 liked this · 1 year ago
hoshi959 liked this · 1 year ago -
 ank-ala reblogged this · 1 year ago
ank-ala reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 x-heesy liked this · 1 year ago
x-heesy liked this · 1 year ago -
 decemberthenemesis reblogged this · 1 year ago
decemberthenemesis reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 decemberthenemesis liked this · 1 year ago
decemberthenemesis liked this · 1 year ago -
 lucylightsblog reblogged this · 1 year ago
lucylightsblog reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 inspirationwithasideoftutorials reblogged this · 1 year ago
inspirationwithasideoftutorials reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 mar-chive reblogged this · 1 year ago
mar-chive reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 a-murder-a-queer-crows reblogged this · 1 year ago
a-murder-a-queer-crows reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 a-murder-a-queer-crows liked this · 1 year ago
a-murder-a-queer-crows liked this · 1 year ago -
 strawberry-arrowtip reblogged this · 1 year ago
strawberry-arrowtip reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 strawberry-arrowtip liked this · 1 year ago
strawberry-arrowtip liked this · 1 year ago -
 natello liked this · 1 year ago
natello liked this · 1 year ago -
 ffrposties reblogged this · 1 year ago
ffrposties reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 sugargutz liked this · 1 year ago
sugargutz liked this · 1 year ago

Sylwester | i will mostly post sketches, because i'm too lazy to end them
196 posts