How Long Did It Take To Build The Rover??
How long did it take to build the rover??
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Spacewalk Recap Told in GIFs
Friday, Oct. 20, NASA astronauts Randy Bresnik and Joe Acaba ventured outside the International Space Station for a 6 hour and 49 minute spacewalk. Just like you make improvements to your home on Earth, astronauts living in space periodically go outside the space station to make updates on their orbiting home.
During this spacewalk, they did a lot! Here’s a recap of their day told in GIFs…
All spacewalks begin inside the space station. Astronauts Paolo Nespoli and Mark Vande Hei helped each spacewalker put on their suit, known as an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU).

They then enter an airlock and regulate the pressure so that they can enter the vacuum of space safely. If they did not regulate the pressure safely, the astronauts could experience something referred to as “the bends” – similar to scuba divers.
Once the two astronauts exited the airlock and were outside the space station, they went to their respective work stations.

Bresnik replaced a failed fuse on the end of the Dextre robotic arm extension, which helps capture visiting vehicles.

During that time, Acaba set up a portable foot restraint to help him get in the right position to install a new camera.

While he was getting set up, he realized that there was unexpected wearing on one of his safety tethers. Astronauts have multiple safety mechanisms for spacewalking, including a “jet pack” on their spacesuit. That way, in the unlikely instance they become untethered from the station, the are able to propel back to safety.

Bresnik was a great teammate and brought Acaba a spare safety tether to use.

Once Acaba secured himself in the foot restraint that was attached to the end of the station’s robotic arm, he was maneuvered into place to install a new HD camera. Who was moving the arm? Astronauts inside the station were carefully moving it into place!
And, ta da! Below you can see one of the first views from the new enhanced HD camera…(sorry, not a GIF).

After Acaba installed the new HD camera, he repaired the camera system on the end of the robotic arm’s hand. This ensures that the hand can see the vehicles that it’s capturing.

Bresnik, completed all of his planned tasks and moved on to a few “get ahead” tasks. He first started removing extra thermal insulation straps around some spare pumps. This will allow easier access to these spare parts if and when they’re needed in the future.

He then worked to install a new handle on the outside of space station. That’s a space drill in the above GIF.

After Acaba finished working on the robotic arm’s camera, he began greasing bearings on the new latching end effector (the arm’s “hand”), which was just installed on Oct. 5.

The duo completed all planned spacewalk tasks, cleaned up their work stations and headed back to the station’s airlock.

Once safely inside the airlock and pressure was restored to the proper levels, the duo was greeted by the crew onboard.

They took images of their spacesuits to document any possible tears, rips or stains, and took them off.

Coverage ended at 2:36 p.m. EDT after 6 hours and 49 minutes. We hope the pair was able to grab some dinner and take a break!
You can watch the entire spacewalk HERE, or follow @Space_Station on Twitter and Instagram for regular updates on the orbiting laboratory.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Pew! Pew! Pew!
Imagine slow-motion fireworks that started exploding 170 years ago and are still continuing. This type of firework is not launched into Earth's atmosphere, but rather into space by a doomed super-massive star, called Eta Carinae.
Enjoy the the latest view from our Hubble Space Telescope.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

A cluster of newborn stars herald their birth in this interstellar picture obtained with our Spitzer Space Telescope. These bright young stars are found in a rosebud-shaped (and rose-colored) nebulosity. The star cluster and its associated nebula are located at a distance of 3300 light-years in the constellation Cepheus.
A recent census of the cluster reveals the presence of 130 young stars. The stars formed from a massive cloud of gas and dust that contains enough raw materials to create a thousand Sun-like stars. In a process that astronomers still poorly understand, fragments of this molecular cloud became so cold and dense that they collapsed into stars. Most stars in our Milky Way galaxy are thought to form in such clusters.
The Spitzer Space Telescope image was obtained with an infrared array camera that is sensitive to invisible infrared light at wavelengths that are about ten times longer than visible light. In this four-color composite, emission at 3.6 microns is depicted in blue, 4.5 microns in green, 5.8 microns in orange, and 8.0 microns in red. The image covers a region that is about one quarter the size of the full moon.
As in any nursery, mayhem reigns. Within the astronomically brief period of a million years, the stars have managed to blow a large, irregular bubble in the molecular cloud that once enveloped them like a cocoon. The rosy pink hue is produced by glowing dust grains on the surface of the bubble being heated by the intense light from the embedded young stars. Upon absorbing ultraviolet and visible-light photons produced by the stars, the surrounding dust grains are heated and re-emit the energy at the longer infrared wavelengths observed by Spitzer. The reddish colors trace the distribution of molecular material thought to be rich in hydrocarbons.
The cold molecular cloud outside the bubble is mostly invisible in these images. However, three very young stars near the center of the image are sending jets of supersonic gas into the cloud. The impact of these jets heats molecules of carbon monoxide in the cloud, producing the intricate green nebulosity that forms the stem of the rosebud.
Not all stars are formed in clusters. Away from the main nebula and its young cluster are two smaller nebulae, to the left and bottom of the central 'rosebud,'each containing a stellar nursery with only a few young stars.
Astronomers believe that our own Sun may have formed billions of years ago in a cluster similar to this one. Once the radiation from new cluster stars destroys the surrounding placental material, the stars begin to slowly drift apart.
Additional information about the Spitzer Space Telescope is available at http://www.spitzer.caltech.edu.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Our Weird and Wonderful Galaxy of Black Holes
Black holes are hard to find. Like, really hard to find. They are objects with such strong gravity that light can’t escape them, so we have to rely on clues from their surroundings to find them.
When a star weighing more than 20 times the Sun runs out of fuel, it collapses into a black hole. Scientists estimate that there are tens of millions of these black holes dotted around the Milky Way, but so far we’ve only identified a few dozen. Most of those are found with a star, each circling around the other. Another name for this kind of pair is a binary system.That’s because under the right circumstances material from the star can interact with the black hole, revealing its presence.
The visualization above shows several of these binary systems found in our Milky Way and its neighboring galaxy. with their relative sizes and orbits to scale. The video even shows each system tilted the way we see it here from our vantage point on Earth. Of course, as our scientists gather more data about these black holes, our understanding of them may change.

If the star and black hole orbit close enough, the black hole can pull material off of its stellar companion! As the material swirls toward the black hole, it forms a flat ring called an accretion disk. The disk gets very hot and can flare, causing bright bursts of light.

V404 Cygni, depicted above, is a binary system where a star slightly smaller than the Sun orbits a black hole 10 times its mass in just 6.5 days. The black hole distorts the shape of the star and pulls material from its surface. In 2015, V404 Cygni came out of a 25-year slumber, erupting in X-rays that were initially detected by our Swift satellite. In fact, V404 Cygni erupts every couple of decades, perhaps driven by a build-up of material in the outer parts of the accretion disk that eventually rush in.

In other cases, the black hole’s companion is a giant star with a strong stellar wind. This is like our Sun’s solar wind, but even more powerful. As material rushes out from the companion star, some of it is captured by the black hole’s gravity, forming an accretion disk.

A famous example of a black hole powered by the wind of its companion is Cygnus X-1. In fact, it was the first object to be widely accepted as a black hole! Recent observations estimate that the black hole’s mass could be as much as 20 times that of our Sun. And its stellar companion is no slouch, either. It weighs in at about 40 times the Sun.

We know our galaxy is peppered with black holes of many sizes with an array of stellar partners, but we've only found a small fraction of them so far. Scientists will keep studying the skies to add to our black hole menagerie.
Curious to learn more about black holes? Follow NASA Universe on Twitter and Facebook to keep up with the latest from our scientists and telescopes.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Two Steps Forward in the Search for Life on Mars
We haven’t found aliens but we are a little further along in our search for life on Mars thanks to two recent discoveries from our Curiosity Rover.

We detected organic molecules at the harsh surface of Mars! And what’s important about this is we now have a lot more certainty that there’s organic molecules preserved at the surface of Mars. We didn’t know that before.
One of the discoveries is we found organic molecules just beneath the surface of Mars in 3 billion-year-old sedimentary rocks.

Second, we’ve found seasonal variations in methane levels in the atmosphere over 3 Mars years (nearly 6 Earth years). These two discoveries increase the chances that the record of habitability and potential life has been preserved on the Red Planet despite extremely harsh conditions on the surface.

Both discoveries were made by our chem lab that rides aboard the Curiosity rover on Mars.

Here’s an image from when we installed the SAM lab on the rover. SAM stands for “Sample Analysis at Mars” and SAM did two things on Mars for this discovery.
One - it tested Martian rocks. After the arm selects a sample of pulverized rock, it heats up that sample and sends that gas into the chamber, where the electron stream breaks up the chemicals so they can be analyzed.
What SAM found are fragments of large organic molecules preserved in ancient rocks which we think come from the bottom of an ancient Martian lake. These organic molecules are made up of carbon and hydrogen, and can include other elements like nitrogen and oxygen. That’s a possible indicator of ancient life…although non-biological processes can make organic molecules, too.
The other action SAM did was ‘sniff’ the air.

When it did that, it detected methane in the air. And for the first time, we saw a repeatable pattern of methane in the Martian atmosphere. The methane peaked in the warm, summer months, and then dropped in the cooler, winter months.

On Earth, 90 percent of methane is produced by biology, so we have to consider the possibility that Martian methane could be produced by life under the surface. But it also could be produced by non-biological sources. Right now, we don’t know, so we need to keep studying the Mars!

One of our upcoming Martian missions is the InSight lander. InSight, short for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is a Mars lander designed to give the Red Planet its first thorough checkup since it formed 4.5 billion years ago. It is the first outer space robotic explorer to study in-depth the "inner space" of Mars: its crust, mantle, and core.
Finding methane in the atmosphere and ancient carbon preserved on the surface gives scientists confidence that our Mars 2020 rover and ESA’s (European Space Agency's) ExoMars rover will find even more organics, both on the surface and in the shallow subsurface.
Read the full release on today’s announcement HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
It’s Pi Day!
Pi Day, the informal holiday beloved by math enthusiasts — and even by the math averse — is here! March 14 marks the yearly celebration of the mathematical constant π (pi).

What is Pi?
Pi (3.1415….) is the ratio of circumference to diameter in a circle. Any time you want to find out the distance around a circle when you have the distance across it, you will need this formula.
Despite its frequent appearance in math and science, you can’t write pi as a simple fraction or calculate it by dividing two integers. For this reason, pi is said to be “irrational.” Pi’s digits extend infinitely and without any pattern, adding to its intrigue and mystery.
How Do We Use Pi at NASA?

Measurements: Pi can be used to make measurements – like perimeter, area and volume.
For example, sometimes we use lasers to explode ice samples and study their composition. In this scenario, we can uses pi to calculate the width of the laser beam, which in turn can be used to calculate the amount of energy, or fluence, that hits the ice sample. A larger fluence equals a bigger explosion in the ice.

Commanding Rovers: Pi is also used every day commanding rovers on the Red Planet. Everything from taking images, turning the wheels, driving around, operating the robotic arm and even talking to Earth!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Forecasting D-Day From Above

Image Credit: Department of Transportation. U.S. Coast Guard. Office of Public and International Affairs
It was the raw courage of the more than 160,000 Allied troops who stormed an 80-kilometer (50-mile) stretch of heavily fortified beaches in Normandy, France, that made victory on D-Day possible. But without the sound advice of meteorologists and geologists working behind the scenes, one of the most consequential battles in human history could have gone quite differently.
As D-Day neared, the American meteorologists predicted fair weather on June 5 and pushed for invasion, based on a forecasting method that gave great weight to historical weather conditions for a given date and location. The British forecasters took a different approach, focusing instead on analyzing measurements of temperature, pressure, and humidity to try to map out weather fronts. Unlike the Americans, the British teams predicted low clouds and stormy weather on June 5. At the last minute, Captain James Martin Stagg, the highest ranking of the meteorologists, convinced Eisenhower to postpone the invasion.

NASA Earth Observatory images by Joshua Stevens, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey
Meanwhile, on the other side of the English Channel, German meteorologists had come to the same conclusion—and then some. Their forecasters had predicted that gale-force winds would arrive on June 5 and persist until mid-June. The Germans were so confident that the Allies would not dare attack that they allowed many soldiers to leave their posts on the beaches and take part in war games in Rennes, France. Field Marshal Erwin Rommel felt comfortable enough to return to Germany to deliver a pair of shoes to his wife as a birthday present.

Image Credit: Department of Defense. Department of the Army. Office of the Deputy Chief of Staff for Operations. U.S. Army Audiovisual Center. ca. 1974-5/15/1984
When the first paratroopers were dropped behind enemy lines around midnight and the first wave of Allied boats began to swarm the beaches at dawn on June 6, the weather was still far from ideal. Cloud cover meant many paratroopers ended up in the wrong locations, and rough seas and high winds made the task of landing boats and unloading tanks a terrible challenge. But by noon the skies cleared, just as the Allied meteorologists had predicted. The Germans, meanwhile, had been caught off guard. That day the Allies endured thousands of causalities, but they established a toehold in France that they would never give up.

NASA Earth Observatory images by Joshua Stevens, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey
An enormous amount of scientific expertise went into even the most unscientific of tasks, like rolling a tank up the Normandy beaches. Prior to the invasion, Allied military planners studied nearly one million aerial photographs of the shores of Normandy to find the best landing sites. The aerial photographs would have looked something like the Landsat 8 images shown above. Acquired by the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on July 15, 2018, these image offer a top-down view of the sandy Normandy beaches that were center stage on D-Day.
Read the full story: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/145143/forecasting-d-day
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What’s On Board the Next SpaceX Cargo Launch?
Cargo and supplies are scheduled to launch to the International Space Station on Monday, July 18 at 12:45 a.m. EDT. The SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft will liftoff from our Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

Among the arriving cargo is the first of two international docking adapters, which will allow commercial spacecraft to dock to the station when transporting astronauts in the near future as part of our Commercial Crew Program.

This metallic ring, big enough for astronauts and cargo to fit through represents the first on-orbit element built to the docking measurements that are standardized for all the spacecraft builders across the world.

Its first users are expected to be the Boeing Starliner and SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft, which are both now in development.
What About the Science?!
Experiments launching to the station range from research into the effects of microgravity on the human body, to regulating temperature on spacecraft. Take a look at a few:
A Space-based DNA Sequencer

DNA testing aboard the space station typically requires collecting samples and sending them back to Earth to be analyzed. Our Biomolecule Sequencer Investigation will test a new device that will allow DNA sequencing in space for the first time! The samples in this first test will be DNA from a virus, a bacteria and a mouse.
How big is it? Picture your smartphone…then cut it in half. This miniature device has the potential to identify microbes, diagnose diseases and evaluate crew member health, and even help detect DNA-based life elsewhere in the solar system.
OsteoOmics
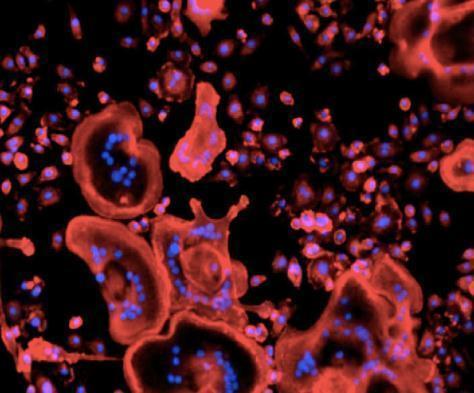
OsteoOmics is an experiment that will investigate the molecular mechanisms that dictate bone loss in microgravity. It does this by examining osteoblasts, which form bone; and osteoclasts, which dissolves bone. New ground-based studies are using magnetic levitation equipment to simulate gravity-related changes. This experiment hopes to validate whether this method accurately simulates the free-fall conditions of microgravity.
Results from this study could lead to better preventative care or therapeutic treatments for people suffering bone loss, both on Earth and in space!
Heart Cells Experiment

The goals of the Effects of Microgravity on Stem Cell-Derived Heart Cells (Heart Cells) investigation include increasing the understanding of the effects of microgravity on heart function, the improvement of heart disease modeling capabilities and the development of appropriate methods for cell therapy for people with heart disease on Earth.
Phase Change Material Heat Exchanger (PCM HX)

The goal of the Phase Change Material Heat Exchanger (PCM HX) project is to regulate internal spacecraft temperatures. Inside this device, we're testing the freezing and thawing of material in an attempt to regulate temperature on a spacecraft. This phase-changing material (PCM) can be melted and solidified at certain high heat temperatures to store and release large amounts of energy.
Watch Launch!
Live coverage of the SpaceX launch will be available starting at 11:30 p.m. EDT on Sunday, July 17 via NASA Television.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
How do blackholes form and how do they move ?

Let's Explore a Metal-Rich Asteroid 🤘
Between Mars and Jupiter, there lies a unique, metal-rich asteroid named Psyche. Psyche’s special because it looks like it is part or all of the metallic interior of a planetesimal—an early planetary building block of our solar system. For the first time, we have the chance to visit a planetary core and possibly learn more about the turbulent history that created terrestrial planets.
Here are six things to know about the mission that’s a journey into the past: Psyche.

1. Psyche could help us learn more about the origins of our solar system.
After studying data from Earth-based radar and optical telescopes, scientists believe that Psyche collided with other large bodies in space and lost its outer rocky shell. This leads scientists to think that Psyche could have a metal-rich interior, which is a building block of a rocky planet. Since we can’t pierce the core of rocky planets like Mercury, Venus, Mars, and our home planet, Earth, Psyche offers us a window into how other planets are formed.

2. Psyche might be different than other objects in the solar system.
Rocks on Mars, Mercury, Venus, and Earth contain iron oxides. From afar, Psyche doesn’t seem to feature these chemical compounds, so it might have a different history of formation than other planets.
If the Psyche asteroid is leftover material from a planetary formation, scientists are excited to learn about the similarities and differences from other rocky planets. The asteroid might instead prove to be a never-before-seen solar system object. Either way, we’re prepared for the possibility of the unexpected!

3. Three science instruments and a gravity science investigation will be aboard the spacecraft.
The three instruments aboard will be a magnetometer, a gamma-ray and neutron spectrometer, and a multispectral imager. Here’s what each of them will do:
Magnetometer: Detect evidence of a magnetic field, which will tell us whether the asteroid formed from a planetary body
Gamma-ray and neutron spectrometer: Help us figure out what chemical elements Psyche is made of, and how it was formed
Multispectral imager: Gather and share information about the topography and mineral composition of Psyche
The gravity science investigation will allow scientists to determine the asteroid’s rotation, mass, and gravity field and to gain insight into the interior by analyzing the radio waves it communicates with. Then, scientists can measure how Psyche affects the spacecraft’s orbit.

4. The Psyche spacecraft will use a super-efficient propulsion system.
Psyche’s solar electric propulsion system harnesses energy from large solar arrays that convert sunlight into electricity, creating thrust. For the first time ever, we will be using Hall-effect thrusters in deep space.

5. This mission runs on collaboration.
To make this mission happen, we work together with universities, and industry and NASA to draw in resources and expertise.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory manages the mission and is responsible for system engineering, integration, and mission operations, while NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Services Program manages launch operations and procured the SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket.
Working with Arizona State University (ASU) offers opportunities for students to train as future instrument or mission leads. Mission leader and Principal Investigator Lindy Elkins-Tanton is also based at ASU.
Finally, Maxar Technologies is a key commercial participant and delivered the main body of the spacecraft, as well as most of its engineering hardware systems.

6. You can be a part of the journey.
Everyone can find activities to get involved on the mission’s webpage. There's an annual internship to interpret the mission, capstone courses for undergraduate projects, and age-appropriate lessons, craft projects, and videos.
You can join us for a virtual launch experience, and, of course, you can watch the launch with us on Oct. 12, 2023, at 10:16 a.m. EDT!
For official news on the mission, follow us on social media and check out NASA’s and ASU’s Psyche websites.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
-
 watch reblogged this · 1 year ago
watch reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 alfaazbrothersak47 liked this · 4 years ago
alfaazbrothersak47 liked this · 4 years ago -
 metaldinleyenametal liked this · 4 years ago
metaldinleyenametal liked this · 4 years ago -
 shailendra65631 reblogged this · 4 years ago
shailendra65631 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 shailendra65631 liked this · 4 years ago
shailendra65631 liked this · 4 years ago -
 jchapa13 liked this · 4 years ago
jchapa13 liked this · 4 years ago -
 dragons-barb liked this · 4 years ago
dragons-barb liked this · 4 years ago -
 galladon reblogged this · 4 years ago
galladon reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 danny1234 liked this · 4 years ago
danny1234 liked this · 4 years ago -
 ourannaodessa liked this · 4 years ago
ourannaodessa liked this · 4 years ago -
 cyare-fi liked this · 4 years ago
cyare-fi liked this · 4 years ago -
 joostacheinthemaking liked this · 4 years ago
joostacheinthemaking liked this · 4 years ago -
 delightfulpaperpost liked this · 4 years ago
delightfulpaperpost liked this · 4 years ago -
 spacenerd84 liked this · 4 years ago
spacenerd84 liked this · 4 years ago -
 jcexe liked this · 4 years ago
jcexe liked this · 4 years ago -
 yuiko2627 liked this · 4 years ago
yuiko2627 liked this · 4 years ago -
 manebioniclegali reblogged this · 4 years ago
manebioniclegali reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 hizrah liked this · 4 years ago
hizrah liked this · 4 years ago -
 delicatemusictale liked this · 4 years ago
delicatemusictale liked this · 4 years ago -
 aero-cosmo-blog liked this · 4 years ago
aero-cosmo-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 flamingspacepigeon liked this · 4 years ago
flamingspacepigeon liked this · 4 years ago -
 chocolateforyou liked this · 4 years ago
chocolateforyou liked this · 4 years ago -
 arius-starwalker-1412 liked this · 4 years ago
arius-starwalker-1412 liked this · 4 years ago -
 rosaliachristian liked this · 4 years ago
rosaliachristian liked this · 4 years ago -
 sunfogo liked this · 4 years ago
sunfogo liked this · 4 years ago -
 lesbiangummybearmafia liked this · 4 years ago
lesbiangummybearmafia liked this · 4 years ago -
 etfoxzi liked this · 4 years ago
etfoxzi liked this · 4 years ago -
 pxlelf liked this · 4 years ago
pxlelf liked this · 4 years ago -
 spacegirlsmom liked this · 4 years ago
spacegirlsmom liked this · 4 years ago -
 realspaceships liked this · 4 years ago
realspaceships liked this · 4 years ago -
 orphaned-account24 liked this · 4 years ago
orphaned-account24 liked this · 4 years ago -
 univ3rsal-s0ul liked this · 4 years ago
univ3rsal-s0ul liked this · 4 years ago -
 princemannikin liked this · 4 years ago
princemannikin liked this · 4 years ago -
 lordofthelarks liked this · 4 years ago
lordofthelarks liked this · 4 years ago -
 trombonesorceress liked this · 4 years ago
trombonesorceress liked this · 4 years ago -
 amazonqueensilver liked this · 4 years ago
amazonqueensilver liked this · 4 years ago -
 lonely-whale-sings liked this · 4 years ago
lonely-whale-sings liked this · 4 years ago -
 superspyelliot liked this · 4 years ago
superspyelliot liked this · 4 years ago -
 arimonsterwolf liked this · 4 years ago
arimonsterwolf liked this · 4 years ago -
 16fahri liked this · 4 years ago
16fahri liked this · 4 years ago -
 artpammy liked this · 4 years ago
artpammy liked this · 4 years ago -
 littolteapot liked this · 4 years ago
littolteapot liked this · 4 years ago -
 interstate-5 liked this · 4 years ago
interstate-5 liked this · 4 years ago -
 louseslayer liked this · 4 years ago
louseslayer liked this · 4 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts