Blizzard 2016 From Space
Blizzard 2016 from Space
As an intense winter storm approaches the mid-Atlantic this weekend, our satellites watch from above. The storm is expected to produce a wade swath of more than 2 feet of snow in some areas.

The below supercomputer simulation crunched the data to provide a look at the flow of clouds from storm systems around the globe, including the developing blizzard across the eastern United States.
This storm won’t only have a snowy impact on the mid-Atlantic region, but will also cause severe weather in the Gulf Coast. Satellites observe extreme rainfall in the area.

Data from NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP satellite and NOAA’s GOES-East satellite are being used to create images and animation of the movement of this powerful storm. For updates, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/nasa-sees-major-winter-storm-headed-for-eastern-us

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Jessica, first of all, I love you. Second, what's it like being a part of the first class that was 50% female?
Thank you! The best part is that I think the fact that our class is 50% female simply reflects how far our society has come, and that is a great thing! To us, there really is no difference on whether or not we are female or male, what backgrounds we come from, etc., we are one team, one family, all contributing to the same cause (which is an extraordinary feeling!). I’m definitely very proud and honored to be part of the 21st astronaut class.
Get to Know the 5 College Teams Sending Their Experiments to Space!
Did you know that YOU (yes you!), can send science experiments to the International Space Station?
To celebrate 20 years of continuous human presence on the International Space Station, NASA STEM on Station is sending five student experiments to the space station through Student Payload Opportunity with Citizen Science (SPOCS). Selected teams will also engage K-12 students as a part of their experiment through citizen-science.
Get to know the 5 college teams sending their experiments to space!
Arkansas State University
Team: A-State Science Support System

Experiment Title: Microgravity Environment Impact on Plastic Biodegradation by Galleria mellonella
Experiment Description: Discover the ability of wax worms to degrade plastics in space.
Why did you propose this experiment?
Our team’s passion for sustainability developed into novel ideas for space travel through biodegradation of plastics.
How will the experiment benefit humankind or future space exploration?
If our experiment is successful, it will “launch” us closer to understanding how to reduce humankind’s plastic footprint on Earth and allow us to safely push farther into unknown planetary habitats.
How have you worked together as a team during the pandemic?
Unknown to each other before the project, our interdisciplinary team formed through virtual communication.
What science fiction character best represents your team and why?
The sandworms of Dune represent our team perfectly considering their importance in space travel, the natural ecological service they provide, and their sheer awesomeness
Columbia University
Team: Columbia Space Initiative

Experiment Title: Characterizing Antibiotic Resistance in Microgravity Environments (CARMEn)
Experiment Description: Discover the impact of mutations on bacteria in microgravity when grown into a biofilm with fungus.
Why did you propose this experiment?
As a highly interdisciplinary team united by our love of outer space, SPOCS was the perfect opportunity to fuse biology, engineering, and education into a meaningful team project.
How will the experiment benefit humankind or future space exploration?
Studying how different microorganisms interact with each other to develop bacterial resistance in space will help improve antibiotic treatments for future Artemis astronauts.
How have you worked together as a team during the pandemic?
Most of our team actually hasn’t ever met in person—we’ve been videoconferencing weekly since May!
What science fiction character best represents your team and why?
Our team is definitely Buzz Lightyear from Toy Story, because we strive to reach infinity (or at least the International Space Station) and beyond!
Stanford University
Team: Stanford Student Space Initiative

Experiment Title: Biopolymer Research for In-Situ Capabilities (BRIC)
Experiment Description: Determine how microgravity impacts the solidification of biobricks.
Why did you propose this experiment?
We have an ongoing project to design and build a machine that turns lunar or Martian soil into bricks, and we want to learn how reduced gravity will impact the process.
How will the experiment benefit humankind or future space exploration?
We are studying an environmentally-friendly concrete alternative that can be used to make structures on Earth and other planets out of on-site, readily available resources.
How have you worked together as a team during the pandemic?
We transitioned our weekly meetings to an online format so that we could continue at our planned pace while maintaining our community.
What science fiction character best represents your team and why?
Like our beloved childhood friend WALL-E, we craftily make inhospitable environments suitable for life with local resources.
University of Idaho
Team: Vandal Voyagers I

Experiment Title: Bacteria Resistant Polymers in Microgravity
Experiment Description: Determine how microgravity impacts the efficacy of bacteria resistant polymers.
Why did you propose this experiment?
The recent emphasis on surface sterility got us thinking about ways to reduce the risk of disease transmission by surfaces on the International Space Station.
How will the experiment benefit humankind or future space exploration?
If successful, the application of proposed polymers can benefit humankind by reducing transmission through high contact surfaces on and off Earth such as hand rails and door handles.
How have you worked together as a team during the pandemic?
We are allowed to work collaboratively in person given we follow the current university COVID guidelines.
What science fiction character best represents your team and why?
Mark Watney from The Martian because he is willing to troubleshoot and problem solve on his own while collaborating with NASA from afar.
University of New Hampshire at Manchester
Team: Team Cooke

Experiment Title: Novel Methods of Antibiotic Discovery in Space (NoMADS)
Experiment Description: Determine how microgravity impacts the amount of bacterium isolates that produce antibiotic metabolites.
Why did you propose this experiment?
To contribute to the limited body of knowledge regarding bacterial resistance and mutations in off-Earth conditions.
How will the experiment benefit humankind or future space exploration?
Understanding how bacteria in the human microbiome and on spacecraft surfaces change can ensure the safe and accurate treatment of bacterial infections in astronauts.
How have you worked together as a team during the pandemic?
Our team continued to evolve our communication methods throughout the pandemic, utilizing frequent remote video conferencing, telecommunications, email, and in-person conferences.
What science fiction character best represents your team and why?
Professor Xavier, the founder of the X-Men, because he also works with mutants and feels that while they are often misunderstood, under the right circumstances they can greatly benefit the world.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Black Scientists and Engineers Past and Present Enable NASA Space Telescope
The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is NASA’s next flagship astrophysics mission, set to launch by May 2027. We’re currently integrating parts of the spacecraft in the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center clean room.
Once Roman launches, it will allow astronomers to observe the universe like never before. In celebration of Black History Month, let’s get to know some Black scientists and engineers, past and present, whose contributions will allow Roman to make history.

Dr. Beth Brown
The late Dr. Beth Brown worked at NASA Goddard as an astrophysicist. in 1998, Dr. Brown became the first Black American woman to earn a Ph.D. in astronomy at the University of Michigan. While at Goddard, Dr. Brown used data from two NASA X-ray missions – ROSAT (the ROentgen SATellite) and the Chandra X-ray Observatory – to study elliptical galaxies that she believed contained supermassive black holes.
With Roman’s wide field of view and fast survey speeds, astronomers will be able to expand the search for black holes that wander the galaxy without anything nearby to clue us into their presence.

Dr. Harvey Washington Banks
In 1961, Dr. Harvey Washington Banks was the first Black American to graduate with a doctorate in astronomy. His research was on spectroscopy, the study of how light and matter interact, and his research helped advance our knowledge of the field. Roman will use spectroscopy to explore how dark energy is speeding up the universe's expansion.

NOTE - Sensitive technical details have been digitally obscured in this photograph.
Sheri Thorn
Aerospace engineer Sheri Thorn is ensuring Roman’s primary mirror will be protected from the Sun so we can capture the best images of deep space. Thorn works on the Deployable Aperture Cover, a large, soft shade known as a space blanket. It will be mounted to the top of the telescope in the stowed position and then deployed after launch. Thorn helped in the design phase and is now working on building the flight hardware before it goes to environmental testing and is integrated to the spacecraft.

Sanetra Bailey
Roman will be orbiting a million miles away at the second Lagrange point, or L2. Staying updated on the telescope's status and health will be an integral part of keeping the mission running. Electronics engineer Sanetra Bailey is the person who is making sure that will happen. Bailey works on circuits that will act like the brains of the spacecraft, telling it how and where to move and relaying information about its status back down to Earth.
Learn more about Sanetra Bailey and her journey to NASA.

Dr. Gregory Mosby
Roman’s field of view will be at least 100 times larger than the Hubble Space Telescope's, even though the primary mirrors are the same size. What gives Roman the larger field of view are its 18 detectors. Dr. Gregory Mosby is one of the detector scientists on the Roman mission who helped select the flight detectors that will be our “eyes” to the universe.
Dr. Beth Brown, Dr. Harvey Washington Banks, Sheri Thorn, Sanetra Bailey, and Dr. Greg Mosby are just some of the many Black scientists and engineers in astrophysics who have and continue to pave the way for others in the field. The Roman Space Telescope team promises to continue to highlight those who came before us and those who are here now to truly appreciate the amazing science to come.

To stay up to date on the mission, check out our website and follow Roman on X and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
What's That Space Rock?
The path through the solar system is a rocky road. Asteroids, comets, Kuiper Belt Objects—all kinds of small bodies of rock, metal and ice are in constant motion as they orbit the Sun. But what’s the difference between them, anyway? And why do these miniature worlds fascinate space explorers so much? The answer is profound: they may hold the keys to better understanding where we all come from. Here’s 10 things to know about the solar system this week:

This picture of Eros, the first of an asteroid taken from an orbiting spacecraft, came from our NEAR mission in February 2000. Image credit: NASA/JPL
1. Asteroids
Asteroids are rocky, airless worlds that orbit our Sun. They are remnants left over from the formation of our solar system, ranging in size from the length of a car to about as wide as a large city. Asteroids are diverse in composition; some are metallic while others are rich in carbon, giving them a coal-black color. They can be “rubble piles,” loosely held together by their own gravity, or they can be solid rocks.
Most of the asteroids in our solar system reside in a region called the main asteroid belt. This vast, doughnut-shaped ring between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter contains hundreds of thousands of asteroids, maybe millions. But despite what you see in the movies, there is still a great deal of space between each asteroid. With all due respect to C3PO, the odds of flying through the asteroid belt without colliding with one are actually pretty good.
Other asteroids (and comets) follow different orbits, including some that enter Earth’s neighborhood. These are called near-Earth objects, or NEOs. We can actually keep track of the ones we have discovered and predict where they are headed. The Minor Planet Center (MPC) and Jet Propulsion Laboratory’s Center for Near Earth Object Studies (CNEOS) do that very thing. Telescopes around the world and in space are used to spot new asteroids and comets, and the MPC and CNEOS, along with international colleagues, calculate where those asteroids and comets are going and determine whether they might pose any impact threat to Earth.
For scientists, asteroids play the role of time capsules from the early solar system, having been preserved in the vacuum of space for billions of years. What’s more, the main asteroid belt may have been a source of water—and organic compounds critical to life—for the inner planets like Earth.

The nucleus of Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko, as seen in January 2015 by the European Space Agency’s Rosetta spacecraft. Image credit: ESA/Rosetta/NAVCAM – CC BY-SA IGO 3.0
2. Comets
Comets also orbit the Sun, but they are more like snowballs than space rocks. Each comet has a center called a nucleus that contains icy chunks of frozen gases, along with bits of rock and dust. When a comet’s orbit brings it close to the Sun, the comet heats up and spews dust and gases, forming a giant, glowing ball called a coma around its nucleus, along with two tails – one made of dust and the other of excited gas (ions). Driven by a constant flow of particles from the Sun called the solar wind, the tails point away from the Sun, sometimes stretching for millions of miles.
While there are likely billions of comets in the solar system, the current confirmed number is 3,535. Like asteroids, comets are leftover material from the formation of our solar system around 4.6 billion years ago, and they preserve secrets from the earliest days of the Sun’s family. Some of Earth’s water and other chemical constituents could have been delivered by comet impacts.

An artist re-creation of a collision in deep space. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
3. Meteoroids
Meteoroids are fragments and debris in space resulting from collisions among asteroids, comets, moons and planets. They are among the smallest “space rocks.” However, we can actually see them when they streak through our atmosphere in the form of meteors and meteor showers.

This photograph, taken by an astronaut aboard the International Space Station, provides the unusual perspective of looking down on a meteor as it passes through the atmosphere. The image was taken on Aug. 13, 2011, during the Perseid meteor shower that occurs every August. Image credit: NASA
4. Meteors
Meteors are meteoroids that fall through Earth’s atmosphere at extremely high speeds. The pressure and heat they generate as they push through the air causes them to glow and create a streak of light in the sky. Most burn up completely before touching the ground. We often refer to them as “shooting stars.” Meteors may be made mostly of rock, metal or a combination of the two.
Scientists estimate that about 48.5 tons (44,000 kilograms) of meteoritic material falls on Earth each day.

The constellation Orion is framed by two meteors during the Perseid shower on Aug. 12, 2018 in Cedar Breaks National Monument, Utah. Image credit: NASA/Bill Dunford
5. Meteor Showers
Several meteors per hour can usually be seen on any given night. Sometimes the number increases dramatically—these events are termed meteor showers. They occur when Earth passes through trails of particles left by comets. When the particles enter Earth’s atmosphere, they burn up, creating hundreds or even thousands of bright streaks in the sky. We can easily plan when to watch meteor showers because numerous showers happen annually as Earth’s orbit takes it through the same patches of comet debris. This year’s Orionid meteor shower peaks on Oct. 21.

An SUV-sized asteroid, 2008TC#, impacted on Oct. 7, 2008, in the Nubian Desert, Northern Sudan. Dr. Peter Jenniskens, NASA/SETI, joined Muawia Shaddas of the University of Khartoum in leading an expedition on a search for samples. Image credit: NASA/SETI/P. Jenniskens
6. Meteorites
Meteorites are asteroid, comet, moon and planet fragments (meteoroids) that survive the heated journey through Earth’s atmosphere all the way to the ground. Most meteorites found on Earth are pebble to fist size, but some are larger than a building.
Early Earth experienced many large meteorite impacts that caused extensive destruction. Well-documented stories of modern meteorite-caused injury or death are rare. In the first known case of an extraterrestrial object to have injured a human being in the U.S., Ann Hodges of Sylacauga, Alabama, was severely bruised by a 8-pound (3.6-kilogram) stony meteorite that crashed through her roof in November 1954.

The largest object in the asteroid belt is actually a dwarf planet, Ceres. This view comes from our Dawn mission. The color is approximately as it would appear to the eye. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UCLA/MPS/DLR/IDA
7. Dwarf Planets
Don’t let the name fool you; despite their small size, dwarf planets are worlds that are just as compelling as their larger siblings. Dwarf planets are defined by astronomers as bodies massive enough to be shaped by gravity into a round or nearly round shape, but they don’t have enough of their own gravitational muscle to clear their path of other objects as they orbit the Sun. In our solar system, dwarf planets are mostly found in the Kuiper Belt beyond Neptune; Pluto is the best-known example. But the largest object in the asteroid belt is the dwarf planet Ceres. Like Pluto, Ceres shows signs of active geology, including ice volcanoes.
8. Kuiper Belt Objects
The Kuiper Belt is a disc-shaped region beyond Neptune that extends from about 30 to 55 astronomical units -- that is, 30 to 55 times the distance from the Earth to the Sun. There may be hundreds of thousands of icy bodies and a trillion or more comets in this distant region of our solar system.

An artist's rendition of the New Horizons spacecraft passing by the Kuiper Belt Object MU69 in January 2019. Image credits: NASA/JHUAPL/SwRI
Besides Pluto, some of the mysterious worlds of the Kuiper Belt include Eris, Sedna, Quaoar, Makemake and Haumea. Like asteroids and comets, Kuiper Belt objects are time capsules, perhaps kept even more pristine in their icy realm.

This chart puts solar system distances in perspective. The scale bar is in astronomical units (AU), with each set distance beyond 1 AU representing 10 times the previous distance. One AU is the distance from the Sun to the Earth, which is about 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers. Neptune, the most distant planet from the Sun, is about 30 AU. Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
9. Oort Cloud Objects
The Oort Cloud is a group of icy bodies beginning roughly 186 billion miles (300 billion kilometers) away from the Sun. While the planets of our solar system orbit in a flat plane, the Oort Cloud is believed to be a giant spherical shell surrounding the Sun, planets and Kuiper Belt Objects. It is like a big, thick bubble around our solar system. The Oort Cloud’s icy bodies can be as large as mountains, and sometimes larger.
This dark, cold expanse is by far the solar system’s largest and most distant region. It extends all the way to about 100,000 AU (100,000 times the distance between Earth and the Sun) – a good portion of the way to the next star system. Comets from the Oort Cloud can have orbital periods of thousands or even millions of years. Consider this: At its current speed of about a million miles a day, our Voyager 1 spacecraft won’t reach the Oort Cloud for more than 300 years. It will then take about 30,000 years for the spacecraft to traverse the Oort Cloud, and exit our solar system entirely.

This animation shows our OSIRIS-REx spacecraft collecting a sample of the asteroid Bennu, which it is expected to do in 2020. Image credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center
10. The Explorers
Fortunately, even though the Oort Cloud is extremely distant, most of the small bodies we’ve been discussing are more within reach. In fact, NASA and other space agencies have a whole flotilla of robotic spacecraft that are exploring these small worlds up close. Our mechanical emissaries act as our eyes and hands in deep space, searching for whatever clues these time capsules hold.
A partial roster of our current or recent missions to small, rocky destinations includes:
OSIRIS-REx – Now approaching the asteroid Bennu, where it will retrieve a sample in 2020 and return it to the Earth for close scrutiny.
New Horizons – Set to fly close to MU69 or “Ultima Thule,” an object a billion miles past Pluto in the Kuiper Belt on Jan. 1, 2019. When it does, MU69 will become the most distant object humans have ever seen up close.
Psyche – Planned for launch in 2022, the spacecraft will explore a metallic asteroid of the same name, which may be the ejected core of a baby planet that was destroyed long ago.
Lucy – Slated to investigate two separate groups of asteroids, called Trojans, that share the orbit of Jupiter – one group orbits ahead of the planet, while the other orbits behind. Lucy is planned to launch in 2021.
Dawn – Finishing up a successful seven-year mission orbiting planet-like worlds Ceres and Vesta in the asteroid belt.
Plus these missions from other space agencies:
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)’s Hayabusa2– Just landed a series of small probes on the surface of the asteroid Ryugu.
The European Space Agency (ESA)’s Rosetta – Orbited the comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko and dispatched a lander to its surface.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Sing About NASA with Our Interns
Each semester, interns at Johnson Space Center (JSC) have the opportunity to contribute to our agency’s missions and help us lead the frontier of human space exploration. Interns at JSC also have the opportunity to enhance their experience through weekly meetings to discuss social and professional development topics, and can also get involved in many different committees.
The intern video committee from each semester comes up with ideas and carries out the entire process of creating a video that puts a creative, youthful spin on spreading NASA messages.
Here are a few highlights from some of the great intern videos that have been created:
Welcome to NASA
“Welcome to NASA” is based off of Flo Rida’s “My House” and was created to raise interest for our Journey to Mars. The lyrics and scenes in the video have been re-imagined in order to inform the public about the amazing work going on at NASA and the Johnson Space Center.
Created in 2016
NASA is Good
This latest intern video is based off of Andy Grammer’s “Honey, I’m Good”. This video is designed as an outreach video to raise interest around the One-Year Mission aboard the International Space Station and the Pathways and Student Intern opportunities.
Created in 2015
NASA Johnson Style
NASA Johnson Style was created as an educational parody of Psy’s "Gangnam Style". The intent of the video is to inform the public about the work being done at Johnson Space Center and throughout the agency.
Created in 2012
I.S.S. Baby
A group of NASA interns collaborated to create the I.S.S Baby video based off of Vanilla Ice’s “Ice, Ice, Baby”. The video was designed as an outreach video to raise interest around the International Space Station.
Created in 2008
There are plenty more JSC intern videos. You can watch more and learn about the work done at JSC and throughout the agency HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Mission Possible: Redirecting an Asteroid
As part of our Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM), we plan to send a robotic spacecraft to an asteroid tens of millions of miles away from Earth, capture a multi-ton boulder and bring it to an orbit near the moon for future crew exploration.
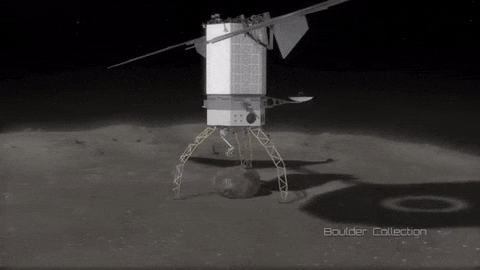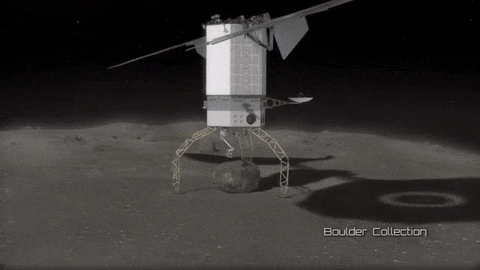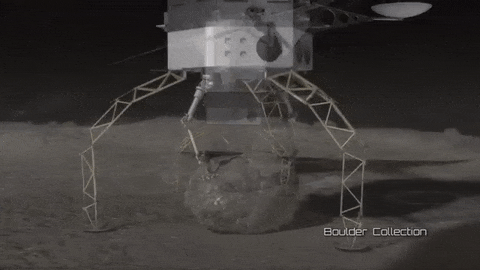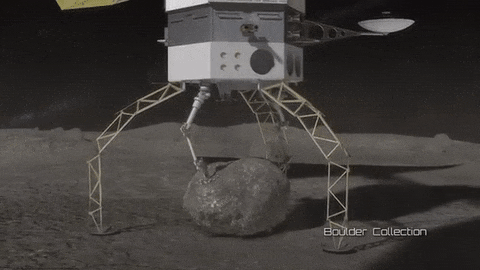
This mission to visit a large near-Earth asteroid is part of our plan to advance the new technologies and spaceflight experience needed for a human mission to the Martian system in the 2030s.
How exactly will it work?
The robotic spacecraft, powered by the most advanced solar electric propulsion system, will travel for about 18 months to the target asteroid.

After the spacecraft arrives and the multi-ton boulder is collected from the surface, the spacecraft will hover near the asteroid to create a gravitational attraction that will slightly change the asteroid’s trajectory.

After the enhanced gravity tractor demonstration is compete, the robotic vehicle will deliver the boulder into a stable orbit near the moon. During the transit, the boulder will be further imaged and studied by the spacecraft.

Astronauts aboard the Orion spacecraft will launch on the Space Launch System rocket to explore the returned boulder.

Orion will dock with the robotic vehicle that still has the boulder in its grasp.

While docked, two crew members on spacewalks will explore the boulder and collect samples to bring back to Earth for further study.

The astronauts and collected samples will return to Earth in the Orion spacecraft.
How will ARM help us send humans to Mars in the 2030s?

This mission will demonstrate future Mars-level exploration missions closer to home and will fly a mission with technologies and real life operational constraints that we’ll encounter on the way to the Red Planet. A few of the capabilities it will help us test include:
Solar Electric Propulsion – Using advanced Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) technologies is an important part of future missions to send larger payloads into deep space and to the Mars system. Unlike chemical propulsion, which uses combustion and a nozzle to generate thrust, SEP uses electricity from solar arrays to create electromagnetic fields to accelerate and expel charged atoms (ions) to create a very low thrust with a very efficient use of propellant.
Trajectory and Navigation – When we move the massive asteroid boulder using low-thrust propulsion and leveraging the gravity fields of Earth and the moon, we’ll validate critical technologies for the future Mars missions.
Advances in Spacesuits – Spacesuits designed to operate in deep space and for the Mars surface will require upgrades to the portable life support system (PLSS). We are working on advanced PLSS that will protect astronauts on Mars or in deep space by improving carbon dioxide removal, humidity control and oxygen regulation. We are also improving mobility by evaluating advances in gloves to improve thermal capacity and dexterity.
Sample Collection and Containment Techniques – This experience will help us prepare to return samples from Mars through the development of new techniques for safe sample collection and containment. These techniques will ensure that humans do not contaminate the samples with microbes from Earth, while protecting our planet from any potential hazards in the samples that are returned.
Rendezvous and Docking Capabilities – Future human missions to Mars will require new capabilities to rendezvous and dock spacecraft in deep space. We will advance the current system we’ve developed with the international partners aboard the International Space Station.
Moving from spaceflight a couple hundred miles off Earth to the proving ground environment (40,000 miles beyond the moon) will allow us to start accumulating experience farther than humans have ever traveled in space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Meet America’s #NewAstronauts
We’re so excited to introduce America’s new astronauts! After evaluating a record number of applications, we’re proud to present our 2017 astronaut class!

These 12 new astronaut candidates were chosen from more than 18,300 people who submitted applications from December 2015 to February 2016. This was more than double the previous record of 8,000 set in 1978.

Meet them…
Kayla Barron

This Washington native graduated from the U.S. Naval Academy with a Bachelor’s degree in Systems Engineering. A Gates Cambridge Scholar, Barron earned a Master’s degree in Nuclear Engineering from the University of Cambridge.
She enjoys hiking, backpacking, running and reading.
Zena Cardman

Zena is a native of Virginia and completed a Bachelor of Science degree in Biology and Master of Science degree in Marine Sciences at The University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. Her research has focused on microorganisms in subsurface environments, ranging from caves to deep sea sediments.
In her free time, she enjoys canoeing, caving, raising backyard chickens and glider flying.
Raja Chari

Raja is an Iowa native and graduated from the U.S. Air Force Academy in 1999 with Bachelor’s degrees in Astronautical Engineering and Engineering Science. He continued on to earn a Master’s degree in Aeronautics and Astronautics from Massachusetts Institute of Technology and graduated from the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School.
He has accumulated more than 2,000 hours of flight time in the F-35, F-15, F-16 and F-18 including F-15E combat missions in Operation Iraqi Freedom.
Matthew Dominick

This Colorado native earned a Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering from the University of San Diego and a Master of Science degree in Systems Engineering from the Naval Postgraduate School. He graduated from U.S. Naval Test Pilot School.
He has more than 1,600 hours of flight time in 28 aircraft, 400 carrier-arrested landigns and 61 combat missions.
Bob Hines

Bob is a Pennsylvania native and earned a Bachelor’s degree in Aerospace Engineering from Boston University. He is a graduate of the U.S. Air Force Test Pilot School, where he earned a Master’s degree in Flight Test Engineering. He continued on to earn a Master’s degree in Aerospace Engineering from the University of Alabama.
During the last five years, he has served as a research pilot at NASA’s Johnson Space Center.
Warren Hoburg

Nicknamed “Woody”, this Pennsylvania native earned a Bachelor’s degree in Aeronautics and Astronautics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and a Doctorate in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science from the University of California, Berkley.
He is an avid rock climber, moutaineer and pilot.
Jonny Kim

This California native trained and operated as a Navy SEAL, completing more than 100 combat operations and earning a Silver Star and Bronze Star with Combat “V”. Afterward, he went on to complete a degree in Mathematics at the University of San Diego and a Doctorate of Medicine at Harvard Medical School.
His interests include spending time with his family, volunteering with non-profit vertern organizations, academic mentoring, working out and learning new skills.
Robb Kulin

Robb is an Alaska native and earned a Bachelor’s degree in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Denver, before going on to complete a Master’s degree in Materials Science and a Doctorate in Engineering at the University of California, San Diego.
He is a private pilot and also enjoys playing piano, photography, packrafting, running, cycling, backcountry skiing and SCUBA diving.
Jasmin Moghbeli

This New York native earned a Bachlor’s degree in Aerospace Engineering with Information Technology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, followed by a Master’s degree in Aerospace Engineering from the Naval Postgraduate School.
She is also a distinguished graduate of the U.S. Naval Test Pilot School and has accumulated mofre than 1,600 hours of flight time and 150 combat missions.
Loral O’Hara

This Texas native earned a Bachelor of Science degree in Aerospace Engineering at the University of Kansas and a Master of Science degree in Aeronautics and Astronautics from Purdue University.
In her free time, she enjoys working in the garage, traveling, surfing, diving, flying, sailing, skiing, hiking/orienteering, caving, reading and painting.
Frank Rubio

Frank is a Florida native and graduated from the U.S. Military Academy and earned a Doctorate of Medicine from the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences.
He is a board certified family physician and flight surgeon. At the time of his selection, he was serving in the 10th Special Forces Group (Airborne).
Jessica Watkins

This Colorado native earned a Bachelor’s degree in Geological and Environmental Sciences at Stanford University, and a Doctorate in Geology from the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA).
She enjoys soccer, rock climbing, skiing and creative writing.

After completing two years of training, the new astronaut candidates could be assigned to missions performing research on the International Space Station, launching from American soil on spacecraft built by commercial companies, and launching on deep space missions on our new Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Spectacular death. Spectacular star. Your crushed heart remains bright from afar. You’re looking at a composite image of the Crab Nebula, located 6,500 light-years away. The white dot in the center — an extremely dense ball of neutrons just 12 miles across but with the same mass as our Sun — is all that remains from a star that exploded in 1054 A.D. Had the blast occurred 50 light-years away, its intense radiation would have wiped out most life forms on Earth. Spectacular death. Spectacular star. We’re grateful we can admire you from afar.
8 Things to Know About Our Commercial Crew Program
Two years after selecting the next generation of American spacecraft and rockets that will launch astronauts to the International Space Station, engineers and spaceflight specialists across our Commercial Crew Program, Boeing and SpaceX are putting in place the elements required for successful missions.

1. The Goal
The goal of our Commercial Crew Program is to return human spaceflight launches to U.S. soil, providing reliable and cost-effective access to low-Earth orbit on systems that meet our safety requirements. To accomplish this goal, we are taking a unique approach by asking private companies, Boeing and SpaceX, to develop human spaceflight systems to take over the task of flying astronauts to station.

2. Multi-User Spaceport
Boeing and SpaceX, like other commercial aerospace companies, are capitalizing on the unique experience and infrastructure along the Space Coast at our Kennedy Space Center and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Kennedy has transitioned from a government-only launch complex to a premier multi-user spaceport. In the coming years, the number of launch providers along the Space Coast is expected to more than double.

3. Innovation
Our expertise has been joined with industry innovations to produce the most advanced spacecraft to ever carry humans into orbit. Each company is developing its own unique systems to meet our safety requirements, and once certified by us, the providers will begin taking astronauts to the space station.

4. Research
With two new spacecraft that can carry up to four astronauts to the International Space Station with each of our missions, the number of resident crew will increase and will double the amount of time dedicated to research. That means new technologies and advances to improve life here on Earth and a better understanding of what it will take for long duration, deep space missions, including to Mars.

5. Crew Training
Astronauts Bob Behnken, Eric Boe, Doug Hurley and Suni Williams have been selected to train to fly flight tests aboard the Boeing CST-100 Starliner and SpaceX Crew Dragon.

The veteran crew have sent time in both spacecraft evaluating and training on their systems. Both providers are responsible for developing every aspect of the mission, from the spacesuits and training, to the rocket and spacecraft.

6. Launch Abort System
Boeing and SpaceX will equip their spacecraft with launch abort systems to get astronauts out of danger . . . FAST!

7. Expedited Delivery
Time-sensitive, critical experiments performed in orbit will be returned to Earth aboard commercial crew spacecraft, and returned to the scientists on Earth in hours, instead of days – before vital results are lost. That means better life and physical science research results, like VEGGIE, heart cells, and protein crystals.

8. Lifeboat
The spacecraft will offer safe and versatile lifeboats for the crew of the space station, whether an emergency on-orbit causes the crew to shelter for a brief time in safety, or leave the orbiting laboratory altogether. Learn more HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up for May?
This month, Jupiter is well placed for evening viewing, Saturn rises before midnight and the moon dances with Venus, Mercury and Mars.

Jupiter climbs higher in the southeast sky earlier in the evening this month, instead of having to wait until midnight for the planet to make an appearance. You can even see with just a pair of binoculars--even the four Galilean moon!

You can even see with just a pair of binoculars--even Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto--the four Galilean moons--as they change position each night!

Our moon appears near Jupiter in the nighttime sky from May 5-8.

The moon joins Venus and Mercury in the eastern sky just before sunrise on May 22 and May 23.

Later in the month, our moon pairs up with Mars in the west-northwest sky on May 26.

Saturn will be visible before midnight in early May, rising about 11:30 p.m. and by 9:30 p.m. later in the month. The best time to see Saturn Saturn is when it’s higher in the sky after midnight near the end of the month.

Using a telescope, you may be able to see Saturn’s cloud bands, or even a glimpse of Saturn’s north polar region--views that were beautifully captured by our Cassini spacecraft.

Watch the full video:
Follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
-
 mostafa18xl liked this · 8 years ago
mostafa18xl liked this · 8 years ago -
 pi-alamode reblogged this · 8 years ago
pi-alamode reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 pi-alamode liked this · 8 years ago
pi-alamode liked this · 8 years ago -
 naboohoney reblogged this · 8 years ago
naboohoney reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 heliosphoenix reblogged this · 8 years ago
heliosphoenix reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 atomsandatoms reblogged this · 8 years ago
atomsandatoms reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 jsbustaman liked this · 9 years ago
jsbustaman liked this · 9 years ago -
 tristanshoard reblogged this · 9 years ago
tristanshoard reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 keialuma reblogged this · 9 years ago
keialuma reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 itsbellaphoenix reblogged this · 9 years ago
itsbellaphoenix reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 itsbellaphoenix liked this · 9 years ago
itsbellaphoenix liked this · 9 years ago -
 mybatista-blog1 liked this · 9 years ago
mybatista-blog1 liked this · 9 years ago -
 sunshineparadiseevans liked this · 9 years ago
sunshineparadiseevans liked this · 9 years ago -
 clrones liked this · 9 years ago
clrones liked this · 9 years ago -
 starchildchampion-blog liked this · 9 years ago
starchildchampion-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 chasingriversong liked this · 9 years ago
chasingriversong liked this · 9 years ago -
 luciferskin reblogged this · 9 years ago
luciferskin reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 rjbailey reblogged this · 9 years ago
rjbailey reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 makemoneyonlineiseasy-com liked this · 9 years ago
makemoneyonlineiseasy-com liked this · 9 years ago -
 kyber-erso reblogged this · 9 years ago
kyber-erso reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 kyber-erso liked this · 9 years ago
kyber-erso liked this · 9 years ago -
 newandcoolername liked this · 9 years ago
newandcoolername liked this · 9 years ago -
 islademaria liked this · 9 years ago
islademaria liked this · 9 years ago -
 minutt-by-minutt liked this · 9 years ago
minutt-by-minutt liked this · 9 years ago -
 rjbailey liked this · 9 years ago
rjbailey liked this · 9 years ago -
 whatislifeandhowdoidoit reblogged this · 9 years ago
whatislifeandhowdoidoit reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 whatislifeandhowdoidoit liked this · 9 years ago
whatislifeandhowdoidoit liked this · 9 years ago -
 libera--me reblogged this · 9 years ago
libera--me reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 heyitssnickers liked this · 9 years ago
heyitssnickers liked this · 9 years ago -
 colinbrooklyn liked this · 9 years ago
colinbrooklyn liked this · 9 years ago -
 boardofcheapandcheerful liked this · 9 years ago
boardofcheapandcheerful liked this · 9 years ago -
 elegant-vibes liked this · 9 years ago
elegant-vibes liked this · 9 years ago -
 playingjax liked this · 9 years ago
playingjax liked this · 9 years ago -
 alexjang09 liked this · 9 years ago
alexjang09 liked this · 9 years ago -
 alitheastronomer reblogged this · 9 years ago
alitheastronomer reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 one-two-seven liked this · 9 years ago
one-two-seven liked this · 9 years ago -
 carol1st liked this · 9 years ago
carol1st liked this · 9 years ago -
 shybearcollector6 reblogged this · 9 years ago
shybearcollector6 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 lunamageice liked this · 9 years ago
lunamageice liked this · 9 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts